Creating SEO-friendly articles for your business online is a big deal. It’s key that you get it right because that’s how you’ll grow your organic visibility. There is an awful lot that goes into writing top-quality, optimised SEO-friendly articles though.
Are you new to SEO? Do you not have the time to participate in long-term courses and get qualified? It doesn’t matter. That’s why we’ve broken down our top 9 tips to make life easy.
Have you heard of SEO? You’re aware that writing SEO-friendly articles can help online businesses. However, you don’t know where to start. You have lots of questions. What should you write? Are people even looking for it?
Follow these 9 tips to create an SEO-friendly article, and then publish! Even once you’ve published, get to grips with the basics of internal linking so people can find your awesome content.
1. Do your keyword research
Keyword research is your first port of call before you write any SEO article. You need to establish how many people are searching for a given topic.
Only then you can write an optimised article to educate those people and offer them helpful content to directly answer their questions. Become the expert people in your industry. Then, people are much more likely to purchase from you.
Learn more about why keyword research is important in content marketing for your business.
You can do keyword research using a tool like Ahrefs or SEMRush. They charge a small fee. Alternatively, you can use Google’s keyword planner for free.
Firstly, enter a few terms into the tool. These should be terms you’d like to write articles about and want to rank for in Google’s SERPs. You will see this data. We’ve highlighted where you can see those in your tool.
- The keyword – the word(s) being searched in Google
- Average monthly searches – how many searches are made every month on average
- Competition or difficulty – how hard it might be to rank (marked by low to high, or 0-100 with 100 being the most difficult)
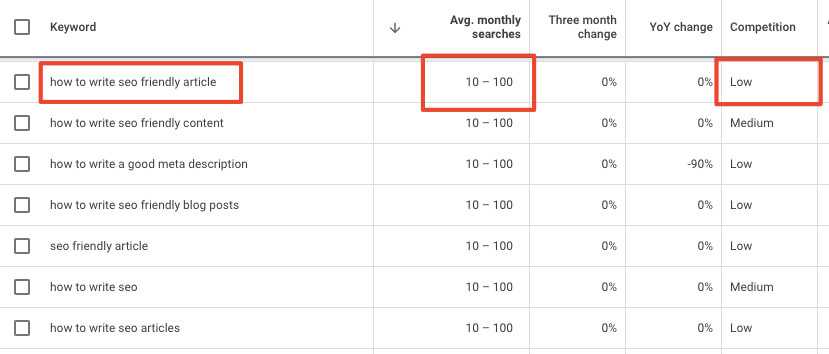
Remember that this can be a time-consuming task for niche industries. For example, is your product or service a new one? If so, there might be fewer people searching for it because they don’t yet know your product exists.
But don’t be discouraged by this. It might take you a little bit longer to find those keyword gems. You’ll get the hang of the keyword research process in next to no time.
2. Get the search intent right
Find the keywords with the correct intent.
What is search intent?
Search intent refers to what the person entering the keyword is looking for. Use our examples below to understand the different types of search intent.
| Search intent | The searcher wants | Example keyword | Content to produce |
| Informational | Information only | ‘What is SEO’‘How to..’‘Guide to…’ | Explainer guide answering this and related questions |
| Navigational | To find and access something specific | ‘SEO agency in…’Brand searches eg ‘Nike store near me’ | Localised landing page |
| Commercial | They intend to buy, but something is stopping them | ‘review..’‘best’ ‘cheapest’ | Product reviewsGuide to which product will help them the mostList of cheapest SEO software in ‘year’ |
| Transactional | Ready to convert | ‘Buy’ ‘vouchers’ ‘for sale’ | Discounts |
Satisfy the searcher’s intent with your content. For example, let’s say your business sells high-end carpet cleaners at an average of €300. Then, let’s say you’ve found search volume for people searching the keyword ‘how do carpet cleaners work’.
Your audience won’t be ready to spend €300 yet. Educate them first. Demonstrate you provide a solution to their problem with helpful, practical content in your SEO-friendly article.
Learn more about the different types of e-commerce content you can and should create for your website.
3. Optimise high-value, core places
Include your keyword in the important places, such as:
- Meta title
- Meta description
- H1
- Other headings where it feels natural
- URL
Why? When Google crawls a page, it looks at each of these to find out what the page is about, and what you want to rank for. So include your keyword in there. Give your article the best chance of ranking.
Where can I see these core places?
Meta data
The meta title and meta description are also known as meta data. It appears in the Google SERPs. Include your target keyword in both of them, and encourage people to click your listing.
Use words like:
- Best
- Latest
- Updated
- Cheapest
- Top
- Popular
The meta title is the text shown in the red square below. The meta description is pointed out by the arrow.
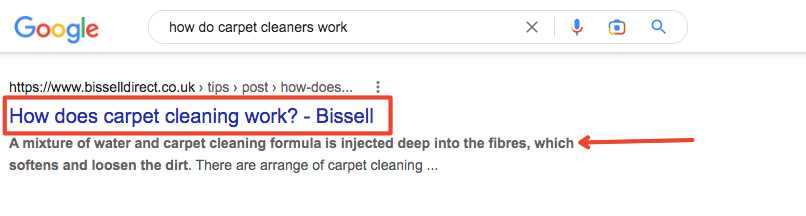
URL
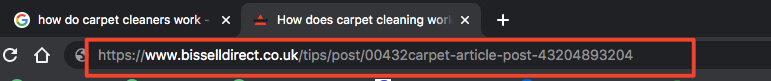
The URL is the specific address your article sits on. Ensure you include the exact match keyword in your URL, and keep your URL nice and clean. Avoid having any numbers in your URL because this doesn’t add any value and looks spammy.
Here is an example. The first URL is optimised, by Bissell Direct, and the second includes numbers and no exact match keyword.

H1
Your H1, or heading 1, is the first heading Google and your searcher reads when the page loads. The heading 1 holds one of the highest level of importance. So, include your keyword, entice them and give them a clear idea of what to expect.
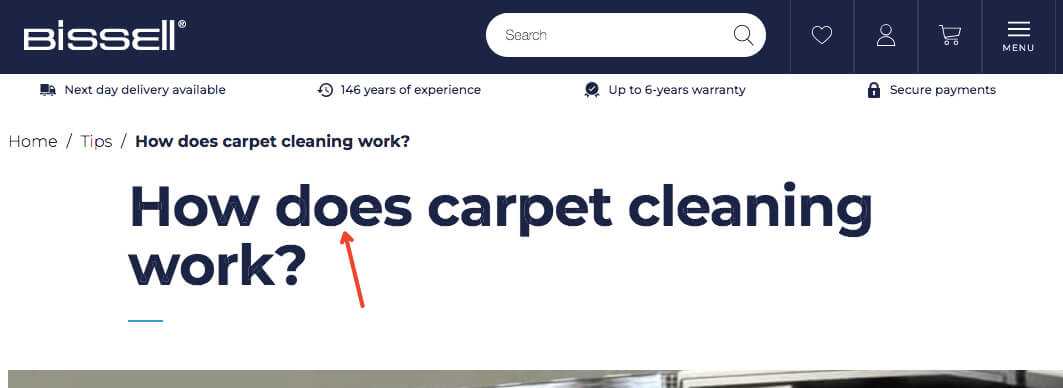
Other headings on the page
Keep your headings relevant and engaging throughout. You can use:
- H2 (heading 2)
- H3
- H4
- H5
- And so on
Google will see the H1 as the most important. The H5 will have the least strength. You should include other related keywords in your H1-H6 headings.
See the example below on how to use other headings.
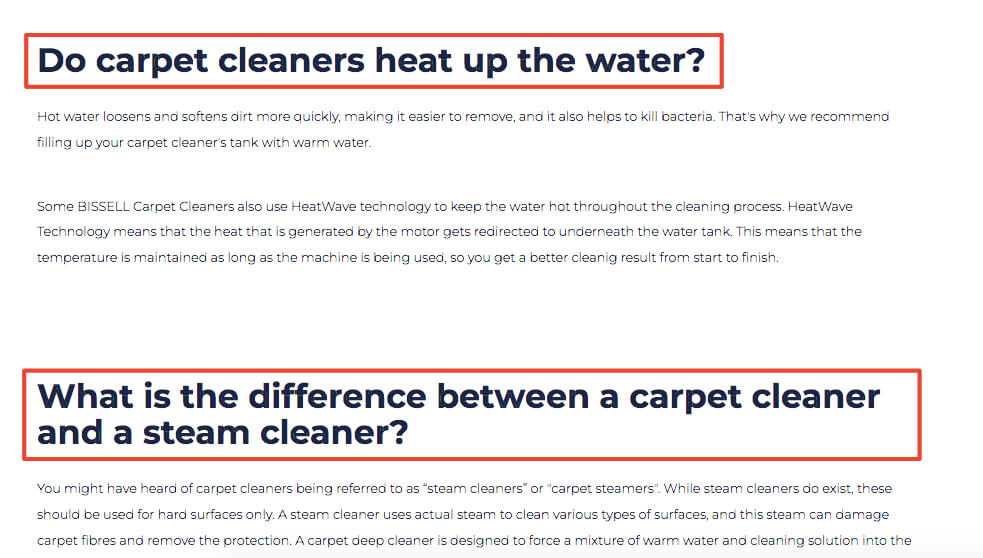
4. Structure your article for real people
Don’t forget people are incredibly time-poor. Google’s research proves that it takes less than a second for people to decide how they feel about a site. It’s the 21st century. So people don’t have the time to read reams and reams of chunky paragraphs.
Improve your article structure. Make it enjoyable and easy to scan.
- Use bullet points
- Add white space
- Reduce bigger paragraphs to smaller ones
- Use headings as a guide
- Use demonstrative images
- Include relevant, helpful videos
- Keep sentences short
- Use easy step-by-step actions
Give people the answers they’re looking for. Give them as quickly and as easily as you can.
5. Check the readability
Don’t include lots of white space and leave it there. Read the content you’ve written aloud and ask yourself the following questions.
- Can I use fewer words and have the same impact?
- Do you run out of breath?
- Do you get tongue-tied?
- Does it not make sense?
- Do you understand it?
- Is it too complicated?
It’s all well and good if you rank in position 1. But people will exit the site if they can’t easily read your copy. Make reading it effortless for your audience.
6. Set the right URL
There are three points to remember when you set your URL when you’re writing an SEO-friendly article.
- include your exact match keyword
- Avoid any clunky, random numbers
- Keep it short and clean
Remember to make your URL accessible. Have you got your blog or tips section accessible in the navigation? If not, add it in, like this example.
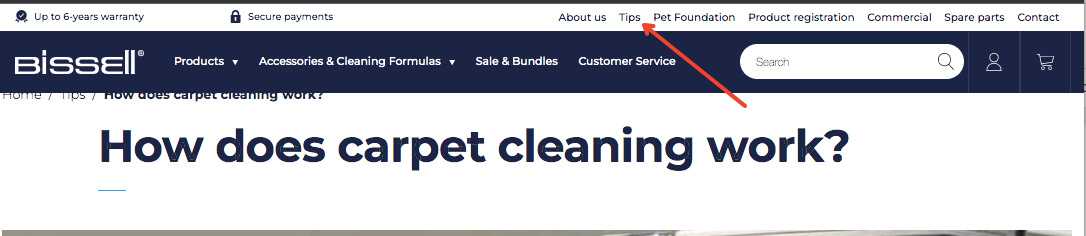
The most important pages need to be easily accessible on desktop and mobile. It’s important for Google to understand internal linking and your website’s hierarchy. On top of that, it makes life easy when people land on your site.
This is called crawl depth. Let’s say you have pages A, B, C and D all linked from the main navigation.
Then, you have pages E, F and G. They can be found by clicking the page in the footer, and then clicking another 5 pages deep. They’re not linked in the navigation or anywhere else on the website.
Google will see A, B, C and D as the most important pages because they’re easy to access. Google will place a much lower importance on the other pages because they’re very difficult for anyone to find. They should be linked to from the main navigation.
Use the correct setup for your article’s URL
Set your URL to dofollow and doindex. Content Management Systems (CMS’) typically have settings you can access and change for this.
There are a couple of ways to check your settings here if you don’t have access to Google Search Console (GSC).
If you do, you can check the index settings of any given page with GSC. You can even request GSC to index a page if it’s not been indexed. But there could be reasons Google isn’t indexing it. For example, here are 3 potential reasons:
The page has thin content on it
Solution: Expand the content and make it unique
The page has duplicate content on it.
Solution: Use a tool like Ahrefs or Screaming Frog to identify where which pages Google is seeing as duplicated.
Are they useful? Make them unique and improve them.
Are they unuseful or outdated? Update them, improve them or redirect them.
The page has been set to noindex.
Solution: Ensure the page is set to ‘index’.
The page is an orphan page.
Solution: Add some internal links to your page. Optimise your anchor text. If possible, add a link from your main navigation.
The page hasn’t been crawled or indexed yet.
Solution: Do all of the above first. Then, if the page doesn’t get crawled or indexed, you can test the indexability in Google Search Console’s URL inspection tool. Then, request it to be indexed. Be sure to check out these tactics to index faster.
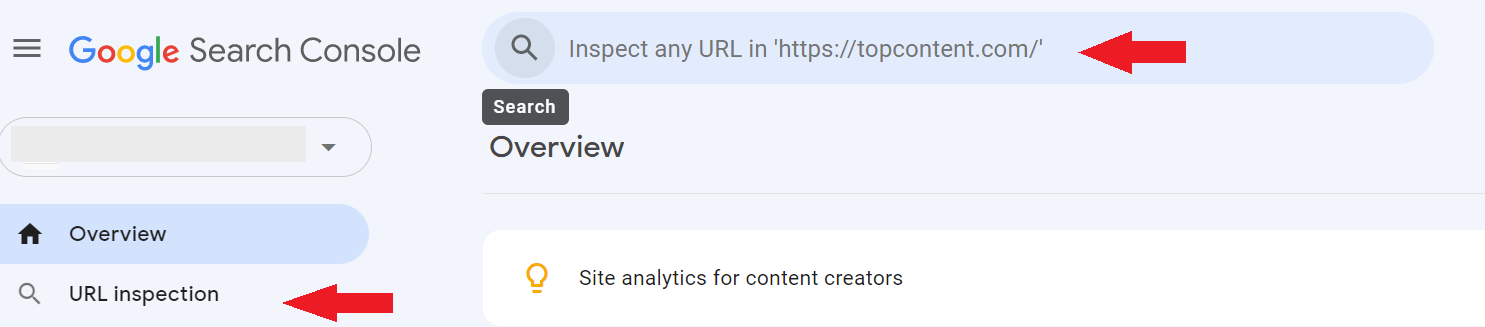
If you don’t have access to Google Search Console, follow these steps.
- Open one of your articles on your website.
- Right-click and select ‘inspect’
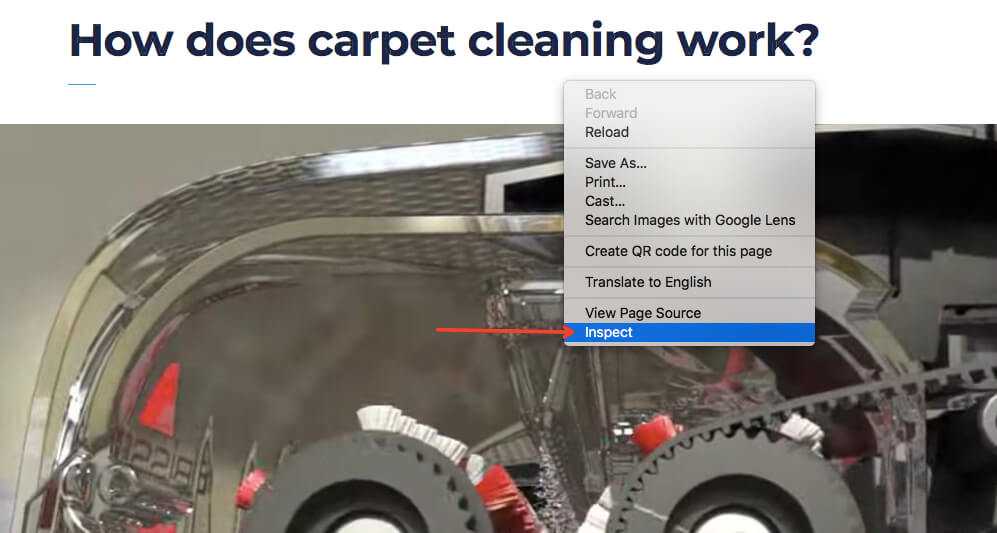
3. Command + F (for Mac) to search and type ‘follow’ or ‘index’
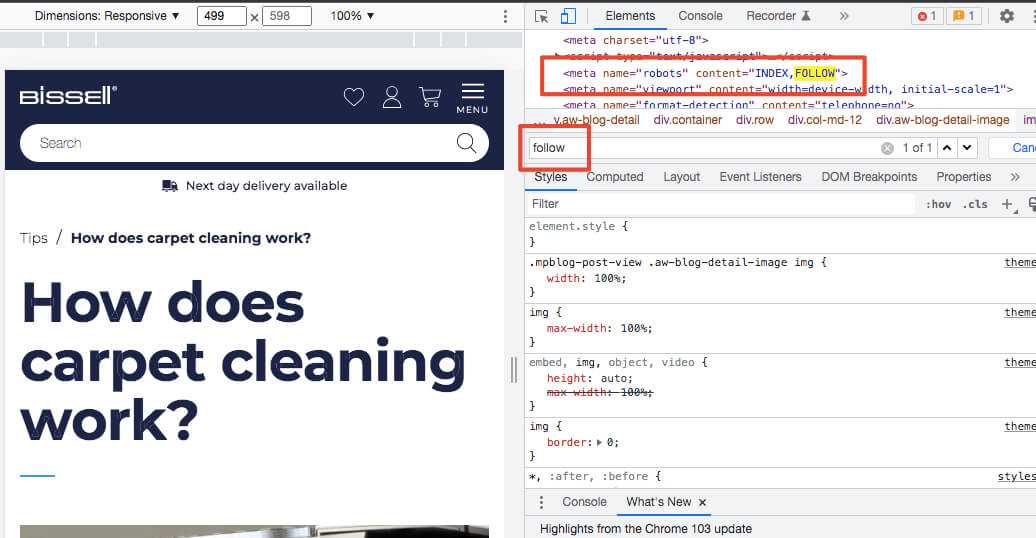
You’re now looking at your website code.
Does it say ‘nofollow’ or ‘noindex’? Change your settings in your CMS or ask a developer for help.
Does it say ‘index’ and ‘follow? You’re good to go!
What do follow and index mean?
‘Follow’ tells Google you trust this page and any links on it. You believe it to be good quality, trustworthy and not spam. This should be the case for your entire website. So, we recommend checking no pages are set to ‘nofollow’.
‘Index’ tells Google you want this page to be indexed. Google should crawl it into its index so that it can rank somewhere. Some pages, like your checkout page, shouldn’t be indexed. Set your SEO articles to ‘index’.
7. Include relevant, optimised images
Did you know that the average attention span is 8 seconds? That means your content needs to be as sharp as possible. So, include relevant images to keep your audience engaged.
Avoid stock images, stick to unique photos
Don’t fill your article with stock photography because it can look generic. Here’s an example.
Your company article instructs your male audience on how to use your new hair product. Don’t find a generic picture of a man with good hair. Instead, take photographs of a man using your product. Your reader will have a visual every step of the way.
Optimise your alt text and file name
Your image alt text describes your image. Your readers won’t see it. They will only see the image. But Google will read the alt text to understand what the image is.
Include an image description, and insert your keyword because you can rank for images in Google’s SERPs. Don’t include your keyword if it doesn’t naturally fit.
For instance, this website below has used their keyword in their image alt text. However, we’d recommend optimising the file name more, like below.
- ‘Inside’ = could be better
- ‘Inside a carpet cleaner’ = describes the image well
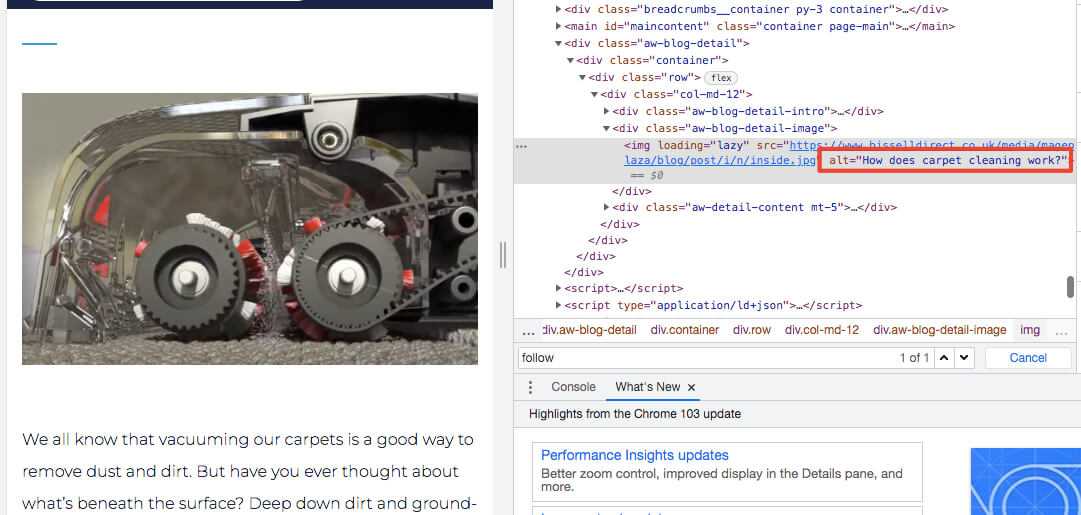
Change the file name of your image. Go to where it’s saved. Right-click and choose rename, like below.
Lazy load your images
Images can take longer than standard text to load on a page, especially if they’re big images or uncompressed. You don’t want to create helpful, optimised images that then slow your page down.
Lazy loading is one way you can ensure your images don’t slow your page down. Your image will load when your reader scrolls that far down the page. Your page should take less than 3 seconds to load. Otherwise, you risk people bouncing.
Ask a developer to lazy load your images.
8. Check if it’s optimised for mobile viewing
Google became mobile first in 2021. That means your website needs to be optimised for people on mobiles as well as desktop devices. If your article’s page takes too long to load on mobile, Google might pick up on this. Google is known to crawl a page by its mobile version. So, check your mobile usability and speed.
You can do this on Google Search Console. You’ll need to log in, validate your website and use the mobile usability checker tool.
IMG
9. Add internal links
Once you have everything set and you’ve published, don’t leave your article as an orphan page.
What’s an orphan page?
An orphan page does not have any internal links.
Why should you add internal links?
When you add an internal link in your main text, the URL is placed on the words you choose to link. Here’s an example from one of our articles. We’ve linked to an article titled ‘Why content quality is more important than keywords’. The anchor text is ‘high-quality content’.
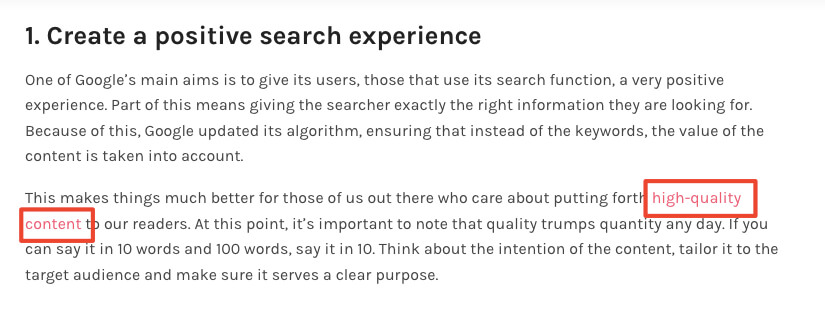
So when Google reads this page, it will also see that there is an internal link to a relevant article the reader might find useful. The anchor text helps Google, and your reader, get an understanding of what that page is about. In this case, it’s high-quality content.
How does this help your reader?
This helps your reader know what to expect when they land on the page. Your reader is less likely to bounce if you educate them correctly about what the article talks about.
How does this help Google?
Google uses your anchor text to distinguish your article’s context. Then, it can rank that linked article. Google also uses the number of internal links as a signal. The quantity of links indicates how important a page is.
Don’t link only once to an article with unoptimised, irrelevant anchor text. Add plenty of relevant internal links across all articles.
There are a few ways you can set up easy internal linking to get you started.
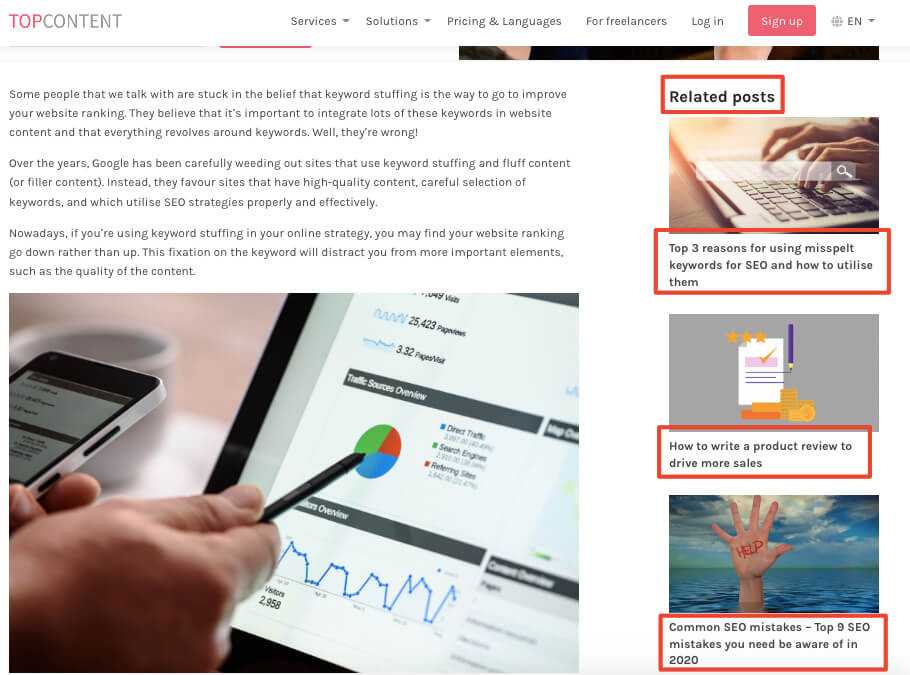
- Add related posts to your blog section
- Categorise your articles
- Get a plugin to recommend link opportunities
You should feel more confident to go about creating an SEO-friendly article. We recommend having a full calendar in place so you can plan which articles will target which of your keywords.
Have you still got questions? We have the answers.
Learn how often you should update your content for businesses. Understand what’s important when it comes to updating your content and how best to go about it.
Get to grips with the different types of content you should be producing. Different phases of the customer journey require different types of content.
Ask yourself when is best to outsource your content and get advice from our team.
Do you need help or don’t have the time? At Topcontent, we have high-quality writers who write SEO-friendly articles to help you rank. We write SEO-friendly web content and SEO-optimised articles to help businesses like yours.
