So much time and effort is put into creating SEO-friendly content, but if your pages aren’t crawlable or indexable, then your content will never stand a chance at ranking. This is why technical SEO is so important.
Technical SEO is all about getting the “behind the scenes” elements of your SEO strategy right. This part of SEO is more search engine-focused (instead of user-focused) and it can have a major impact on how well your website performs and ranks.
Don’t let the word “technical” throw you off though – getting your technical SEO elements up to scratch is a lot easier than many people realize.
This guide will reveal everything you need to know about technical SEO and how to get started with it.
- Technical SEO Guide For Beginners
- What is Technical SEO?
- Technical SEO, On-Page SEO, and Off-Page SEO
- Why is Technical SEO Important?
- How Technical SEO Works
- Elements to Include in Your Technical SEO Strategy
- Setting Up Your Website
- Programming Languages (HTML, CSS, JavaScript)
- Implement an XML Sitemap
- Make the Most of Your Crawl Budget
- Optimize Site Architecture
- Use Canonicalization
- Optimize Your Site for Rendering
- Implement Structured Data
- Enhance Page Speed
- Inspect Blocked Pages
- Be Aware of Thin and Duplicate Content
- Offer a Positive User Experience
- Conclusion
What is Technical SEO?
Technical search engine optimization (SEO) includes any processes you use to optimize a website so that search engines can crawl and index it more easily. Technical SEO is used alongside other SEO strategies (like link-building and content strategies) to help websites perform well in search engines.
While website content has always been a major focus of SEO, technical SEO is more about what happens in the background. This area of SEO is mostly focused on making sure your website is optimized for search engines, instead of just focusing on what it offers the user.
Technical SEO, On-Page SEO, and Off-Page SEO
To understand technical SEO, it’s important to understand the other areas of SEO that exist. Generally, this is broken down into three main areas.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO refers to the content displayed on your web pages. This is what users see and what you can use to tell search engines what your pages are about.
You have the most control over on-page SEO because all of this data can be easily accessed and changed directly on your site. On-page SEO strategies include things like using keywords, meta descriptions, title tags, internal linking, naming URLs, and writing content.
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO refers to what happens outside of your website that adds trust signals to your site. Most notably, this includes things like backlinks, which boost a page’s Pagerank. Off-page SEO is the most difficult element to manage because everything happens off your website. This means you are not in direct control over it.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO is all about making sure your website performs well for search engines. This includes making the website easy to crawl, index, and render. You are still in control over technical SEO elements, although they can be more tricky to manage than other on-page SEO tactics.
Some examples of technical SEO include building structured data on your site, building an XML sitemap, or optimizing your site’s loading speed. We’ll cover a lot more strategies below.
Why is Technical SEO Important?
Your website might have the most interesting, engaging, and well-crafted content on it, but this doesn’t mean search engines will be able to index and rank it well. Good technical SEO performance ensures search engine bots are able to easily crawl and understand your website. This is necessary for achieving top rankings.
If you don’t get your technical SEO right, search engines can’t properly access your website. In this case, don’t expect to make it onto the SERPs – even if your content is amazing.
How Technical SEO Works
There’s a lot that goes into technical SEO. One of the most difficult things to get right is prioritizing which elements of technical SEO to focus on. Some have more impact than others, although all of them add together to boost your site’s organic performance.
When considering your technical SEO strategy, there are five key areas you need to get right. These are:
- Crawlability
- Indexability
- Renderability
- Rankability
- Clickability
1. Website Crawlability
Search engine bots crawl your website in order to gather information about your site and understand what it’s about. This is necessary for search engines to index and rank your pages.
Crawlability forms the foundation of any technical SEO strategy. You need to make sure that all of your web pages are accessible and easy for search engines to navigate.
Search engines grab content from web pages when they perform a crawl, and then use the links on these pages to find even more pages. So, if you want to make your site more “crawlable”, then you’ll need to pay close attention to how accessible each page on your website is.
Good crawlability tactics include optimizing your site’s architecture, using a good URL structure, and creating an XML sitemap (amongst other things).
2. Indexability
After a search engine bot crawls your website, it will start indexing each page based on the topic of the page and how relevant your page is to the topic. You need to get your pages indexed on search engines if you’re going to get them to rank well in SERPs. There are certain tactic you can implement to index your page faster.
Indexing is how a search engine “files” or stores web pages based on certain topics. You can view your page’s index status on Google Search Console.
Improving your website’s indexability could be done by ensuring you don’t have any duplicate content, fixing HTTP errors, making sure search bots can access all pages, and more.
3. Renderability
Your website needs to easily render in search engines in order to make it more accessible. A site that’s more accessible will be able to perform better in the search results.
Improving the renderability of your website comes down to factors like your server performance, page load speed, chains of redirects, page depth, whether you have any orphan pages on your site, and more.
4. Rankability
At this point, search engines can place your website in the SERPs, but you still need to make sure your site is optimized to rank as high as possible. To do this, you need to implement a few technical on-page and off-page SEO elements.
This can include things like your internal and external links, the kind of backlinks your site has or having your site consist of well-planned. content clusters.
5. Clickability
The final goal of SEO is to get as many users clicking on your pages as possible. While CTR involves a lot of “non-technical” on-page SEO tactics, there are still some technical SEO elements you can use.
This could include things like using structured data to gain rich snippets in search results or optimizing your site to win SERP features.
An effective technical SEO strategy involves optimizing your website for each of these five areas.
Elements to Include in Your Technical SEO Strategy
As we’ve already said, there’s a lot that goes into technical SEO. Because there are so many different ranking factors, staying on top of every possible technical SEO element can be tricky.
To help you get started, here are some of the most important (and impactful) steps you can take to boost your technical SEO.
Setting Up Your Website
The first essential step in any technical SEO strategy is setting your website up properly. You want to make sure that every page is working at its best.
First, you’ll need a domain name, then you’ll need to link this to an IP address. A Domain Name Server (DNS) organizes IP addresses, which are basically numbers that help the internet understand and categorize your domain name.
Once this is done, you need to prepare your website to appear in searchers’ web browsers. Here are two essential strategies to do this (which will help kickstart your technical SEO).
URL Structures
Your URL structure is how your URL appears – something that both searchers and search engines use to get information about your web page.
Make sure that your website has a Secure Socket layer (SSL) included in your URL. This is represented by the “S” after “HTTP”. This “S” represents an important security protocol, which will help your search engine performance.
Ensure you also include what your page is about in the URL. This is often done by including your main keyword, such as this URL structure:

Keep URLs short and descriptive, and maintain a consistent URL naming structure across your site.
Breadcrumb Navigation
Breadcrumb navigation marks the path a user takes when navigating your website. Adding breadcrumb navigation to your site will help you maintain a good site infrastructure, which is important for accessibility in search engine crawls. It also improves navigation for the user, as they can quickly return to previous pages.
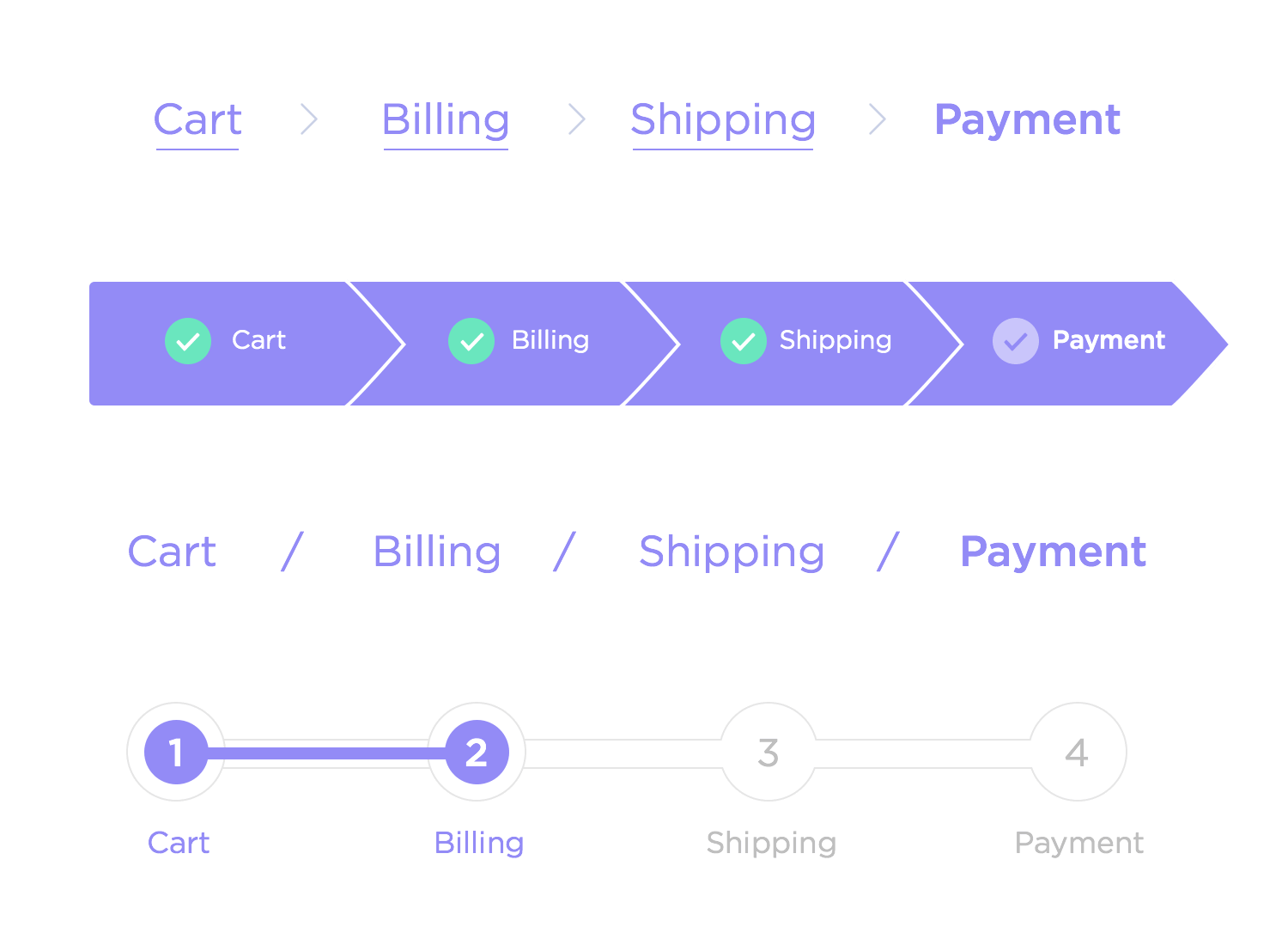
Above is a clear example of a breadcrumb menu (image: justinmind.com)
Programming Languages (HTML, CSS, JavaScript)
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are programming languages that add different elements to your site. Understanding and using the languages correctly is essential for technical SEO.
Don’t worry, you don’t have to become a coding expert. You just have to understand what these different languages do and how to identify them.
- HTML: HyperText Markup Language forms the foundation of your site. This provides the necessary structure for your site to display your web content. If you see any written content on a website, this is made up of HTML.
- JavaScript: JavaScript goes beyond the foundations of your website and adds more functionality. This coding language adds interesting, dynamic elements to a site.
- CSS: Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) makes your website look good. This dictates things like the fonts or colors on your website.
Now you have your website set up and you understand the programming languages that your site consists of. The next steps are to improve crawling, indexing, and rendering on your website.
Implement an XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap reveals your website’s structure. This helps bots understand your website, making it easier for them to crawl your pages. Think of an XML sitemap as a roadmap to your website and how to navigate it from page to page.
You can submit your sitemap to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools to help these search engines with their crawls. Just remember to update your sitemap as you update your website.
Ensure you use the most simple code (HTML) for your main navigation features. This makes it easier for search engines to index your navigation structure. You’ll also need to make sure that mobile and desktop versions of your website use the same navigational paths. If there is a broken navigational link, bots might miss pages when crawling.
Make the Most of Your Crawl Budget
Your crawl budget refers to the pages on your site that bots can crawl. This is limited, so you’ll need to make sure you prioritize your pages for efficient crawling. Here are some good strategies to achieve this:
- Remove any duplicate pages
- Fix broken links
- Ensure your JavaScript and CSS files are crawlable
- Remove outdated or unnecessary content from your site
- Avoid dynamically generated URLs
Optimize Site Architecture
Site architecture reveals how you organize the different pages on your website. A good site architecture will help bots understand how pages relate to each other, which should be done in an intuitive way.
Group together pages that relate to the same topic. You could also group together pages that belong to the same author.
One important thing to understand here is link equity. The closer a page is to your homepage, the more pages will link to them. This gives you more page equity. The more page equity a page has, the more significance it will show search engines.
A great way to use link equity is to build content clusters, with hub and spoke pages. The “hub” page will be the main page on a certain topic, and all “spoke” pages on the same topic will link to the hub page. This gives the hub page more link equity.
The most important thing to remember with site architecture is the more internal links a page has, the higher it will be positioned on your site’s page hierarchy.
Use Canonicalization
Canonicalization is another helpful way you can communicate your important pages to search engines. If your website has the same content on different pages, search engines won’t know which pages to index.
Using the rel=“canonical” tag tells search engines that the page is the “master” version of a piece of content. Basically, it’s a way of pointing your main source of information to search engines so they know which page to index.
If you publish or update content on your suite that has some similarities in it, canonicalization can help you avoid duplicate content issues and ensure every piece of content only has one URL.
A good example of this would be https://websiteexample.com and https://www.websiteexample.com. Both URLs could get indexed separately if you do not use a canonical tag.

Optimize Your Site for Rendering
When a search engine has finished crawling and indexing your content, rendering will happen. If you land on the SERPs and a user clicks on your page, search engines want to ensure users are able to see and interact with your content the way they’re supposed to. This is rendering.
This can get complicated if your site has complex CSS and JavaScript. Try to limit any complex coding elements on each page, or ensure you spend enough time testing these elements so that they render properly.
Implement Structured Data
Structured data is when you apply code to your site that helps search engines understand what type of content is on your web page. This provides a detailed description of the different elements on your web page so that search engines know how to index it. This is done through the use of schema.
If you apply schema markup to your pages, you can gain rich results for your web pages. For example, schema could add product details, ratings, and an image to a product listing on Google:
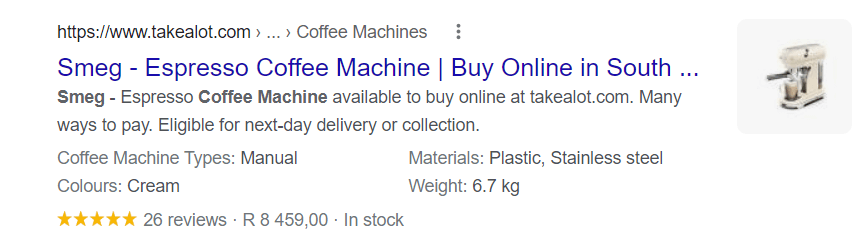
Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper is a useful tool to help you create schema markup elements on your web page. The tool will render structured data for you after you have tagged the different structured data elements. You can then apply this to your web page to boost the page’s structure.
Enhance Page Speed
Page speed is a critical ranking factor. Thanks to more interactive and complex JavaScript and CSS elements on websites today, rendering these dynamic pages in search engines becomes more complex. This is why you need to pay close attention to any page speed issues present on your site.
Start by ensuring you compress any video or image files to make them load faster. Also pay attention to other elements on your site, like rich media or popups, which could affect page speed.
Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals is an important metric for monitoring load speed on your website. Google provides measurements on this through the Core Web Vitals report in Search Console. Any issues present on your site will be displayed in this report.
There are three main elements to Core Web Vitals:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): How long the main portion of the content on a website takes to load
- First Input Delay (FID): This is the response time a page has when a user starts interacting with it, like scrolling or clicking
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Any unexpected shifts in a page layout that happen when the page loads
Inspect Blocked Pages
This goes back to crawlability. You’ll want to inspect any possibly blocked pages on your site, which means the web page is blocking bots from crawling it.
Your goal is to send bots to your preferred pages and ensure they have complete access to these pages. In some cases, you might have blocked pages that you need to unblock, or you might need to block a page to give your preferred page more crawl access.
You can use Google’s robots.txt tester to identify any disallowed pages. Then use the Inspect tool in Google Search Console to find what’s causing these blocked pages.
Be Aware of Thin and Duplicate Content
Thin and duplicate content is a big red flag for search engines. You’ll need to fix or remove any of this content in order to boost your SEO efforts.
Thin Content
Thin content is when a web page doesn’t offer much context to help search engines understand and correctly index the page. This could include a lack of direct, relevant information on the page, or having no internal linking on the page to direct crawlers to other parts of your site.
Duplicate Content
Duplicate content is when you have two or more pages that display the same content. This could be exact content matches or content that targets the same keywords or intent. If this is the case, search engines will struggle to understand which pages to index and prioritize for the search term. This can result in keyword cannibalization, with your site competing with itself for certain search terms. That’s why it is important to find and fix duplicate content.
Offer a Positive User Experience
Technical SEO may be targeted toward search engines, but this doesn’t mean you shouldn’t put your user experience first. Google wants to display content that is most relevant and enjoyable for users, so a great user experience is critical for SEO success.
Here are some ways to enhance UX on your site:
- Mobile-first indexing: When Google crawls the mobile versions of your web pages first. This means it’s important to put a lot of effort into enhancing the experience of your mobile site.
- Accelerated mobile pages (AMP): This is an open-source HTML framework created by Google to help make web content more mobile-friendly. When auditing your site, pay attention to how many of your web pages are AMP links.
- Responsive design: Your website has to respond to the screen it’s being viewed on. You can use CSS to add responsive design to your site, which is essential in today’s mobile-first world.
Conclusion
These are some of the most critical technical SEO elements to add to your site. Once you have strategized and published great content, it’s important that you optimize your web pages so that search engines can access and index them properly.
By getting your on-page, off-page, and technical SEO to work seamlessly together, your website will be on a path straight to the top of the search results!
