Site structure is an essential aspect of search engine optimization.
In fact, the organisation of a website and its pages can impact SEO visibility more than most people realise.
This post covers everything about site structure, including how you can optimise your site to rank higher in search engines, with tips on how to create an effective structure for your website.
What is Site Structure?
Site structure can be defined as the way your content is organised on a website.
It consists of the hierarchy, and connections between different pages, topics, categories, and other elements of your website.
It is important to have an effective site structure in place to ensure that users can easily navigate through your content and search engines are able to crawl it.
Things like taxonomies (such as categories and tags), internal links, navigation menus, breadcrumbs, and URLs help to organise your site.
Why is Site Structure Important?
Having a proper site structure can help ensure that your content is SEO-friendly.
Organising your website in a way that makes it easy for search engine crawlers to understand the relevance of each page will improve the chances of your content being ranked higher in SERPs.
It will also ensure that visitors are able to quickly and easily find the information they’re looking for, which will help improve user experience (an important Google ranking factor).
Having a well-structured website can also make it easier to identify any SEO problems and diagnose issues that are preventing your content from ranking higher.
So, here are the main reasons why site structure is important for SEO:
- It helps search engines understand the relevance of content.
- It makes it easier for users to navigate the site and find what they’re looking for.
- It helps to prevent SEO problems, such as duplicate content or orphaned pages.
- It can increase online visibility by improving the crawlability of a website.
It helps search engines understand the relevance of content
Your website’s structure tells Google which of your pages is most important.
In other words, it helps search engines identify relationships between content on different pages, which can help them understand the relevance of each page.
For example, let’s say you have a blog post about “SEO tips”. If the page includes links to other SEO-related content on your site, Google will be able to understand that this article is connected to other SEO content and should be ranked higher.
It makes it easier for users to navigate the site and find what they’re looking for
A well-structured site structure also helps users quickly find the information they’re looking for.
For example, if you have a hierarchical site structure, it will be easier for users to find content related to their interests by navigating through the different sections of your website.
This will help improve user experience and increase the chances of returning visitors.
It helps to prevent SEO problems, such as duplicate content or orphaned pages
A good site structure can also help to prevent SEO issues, such as duplicate content or orphaned pages, by making sure your content is properly linked and indexed by search engines.
Duplicate content occurs when two or more pages on the same site contain similar or identical content. This is not beneficial as it confuses search engine crawlers and prevents them from being able to properly index your content. That’s why it is important to find duplicate content on your website and fix it.
Orphaned pages are pages that do not have any links to other pages on the site. This means that search engine crawlers will not be able to access these pages, which may prevent them from being indexed.
It can increase online visibility by improving the crawlability of a website
Having an SEO-friendly site structure can also help to increase your online visibility by making it easier for search engines to crawl and index your content.
The crawl budget for each site is limited, so if your website is organised in a way that makes it easier for search engine crawlers to find and understand the content, then this may help improve your rankings.
Types of Website Structure
There are different types of website structures that you can use.
Choose among these popular ones:
- Hierarchical (tree model)
- Flat (sequential model)
- Webbed (network model)
- Database
Hierarchical
In a hierarchical structure, the main content is divided into categories, which helps users navigate the site.
This type of structure is ideal for websites that have a lot of content and need to be organised in a way that makes it easy to find specific information.
For example, if you have a blog about SEO, you might divide your content into categories such as SEO tips, SEO tools, SEO strategies, and SEO trends.
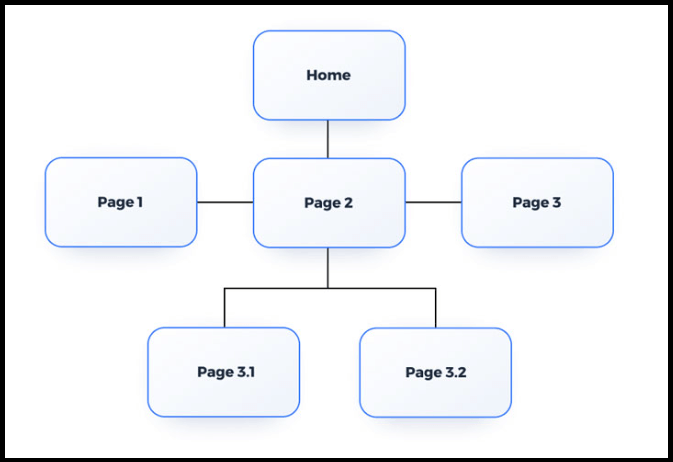
Source: slickplan.com
Flat
In a flat structure, all content is placed on the same page and grouped together by topic. This type of structure can be beneficial for smaller sites that do not have many pages.
Think of business sites with just a few pages, without a blog section, subcategories, or child pages.
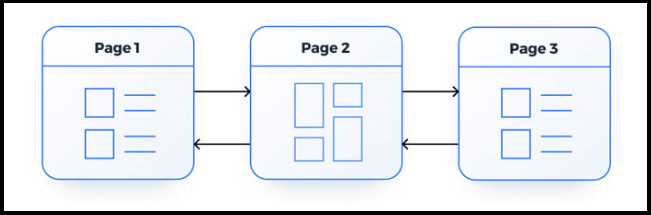
Source: slickplan.com
Webbed
In a webbed structure, content is organised into clusters that are connected with one another.
This type of structure can be beneficial for sites that have large amounts of content and need to be organised in order to help users navigate.
Think of e-commerces or other sites with lots of product pages.
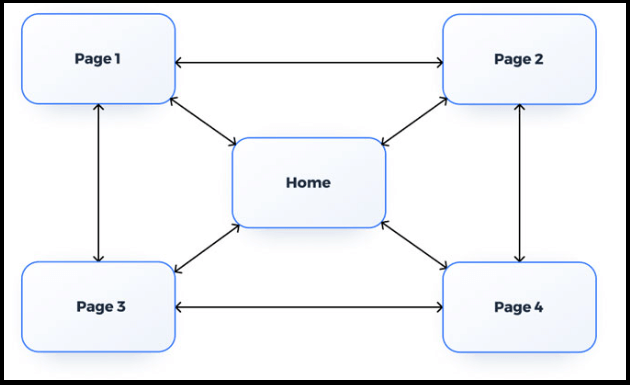
Source: slickplan.com
Database
In a database structure, content is organised into tables that are connected to each other.
This type of structure can be beneficial for sites that have large amounts of complex data and need to be organised in order to make it easier for users to find the information they’re looking for.
Think of websites or applications that include a lot of data, such as customer records or transaction logs.
Ideal Site Structure
The ideal site structure is one that makes it easy for users to find content and make sure that search engine crawlers can easily access, crawl, and index your content.
To achieve this goal, you should focus on creating a hierarchical or webbed structure with clear navigation and logical page hierarchies. This will help to make sure that all content is easily accessible by both users and search engine crawlers.
At the same time, you should also make sure to optimise your page titles and URLs in order to ensure that they are SEO-friendly. This will help search engines to understand the context of your
content and index it properly.
So, how to create the ideal site structure?
A well-organised website is like a pyramid, with different levels of information:
- Homepage
- Navigation (Menu and Breadcrumbs)
- Taxonomies (Categories and Tags)
- Individual Pages and Posts
Homepage
The homepage is the most essential page in your site structure and should contain links to all the main sections of your website.
Navigation
Other than a well-structured homepage, you should have an organised navigation (which consists of the menu and usually, the breadcrumbs).
The menu should be easy to understand and contain all the main pages of your site.
It is essential for visitors to find things easily and it also helps them understand the organisation of your content. That’s why it’s important that all main categories are included in the menu.
Breadcrumbs are beneficial for usability and help with the hierarchy as well. They are used to show the current page’s location within the site structure, making it easier for visitors to navigate and find content quickly.
Taxonomies
These are the main categories and tags of your site structure.
Tags are used to relate content together, while categories help organise the site’s content structure.
If your categories grow too large, you may want to consider dividing them into smaller subcategories for clarification.
For example, if you are running a clothing store and you sell T-shirts, you can add sub-categories like “Men’s T-shirts”, “Women’s T-shirts” and “Kids T-shirts.”
You may also want to use tags to relate content together. For instance, if you have a blog post about “SEO Best Practices” and another one about “SEO Trends for 2022”, you can use the tag “SEO”.
Individual Pages and Posts
Every page or post should have its own unique URL, title, and meta description. This will help search engine crawlers understand the context of each page.
In addition, all pages should be linked to other relevant pages, both in the navigation menu and at the bottom of each page. This will help visitors move around your site more easily and will also help search engine crawlers to find your content.
How to Improve Site Structure
Creating a well-organised site structure is essential for content SEO and should be done right from the start.
Here are some things to keep in mind:
- Site Crawlability
- URL Structure
- Topic Clusters
- Internal Linking
- User Experience
- Core Web Vitals
- Mobile-Friendly
- Page Speed
Site Crawlability
It is important to make sure your site is easy to crawl and index.
You can use SEO tools such as Sitebulb, DeepCrawl, and Screaming Frog SEO Spider to see if there are any crawling or technical issues with your website that might be affecting SEO performance.
Search engine robots (commonly called “spiders”) are in charge of website crawling.
Therefore, the crawl budget is an important step when optimising your website for SEO. A robot needs to crawl pages one by one in order to index them, and it has a limited amount of resources for this task.
To optimise your site’s crawl budget, you can:
- Prevent Google from crawling your non-canonical URLs
- Minimise crawl errors
- Refresh stale content
Prevent Google from Crawling Your Non-Canonical URLs
Non-canonical URLs are pages that can be accessed in multiple ways. You should make sure that all of your pages have only one preferred URL that is used for indexing. This will help you avoid SEO issues and maximise the effectiveness of your pages.
Minimise Crawl Errors
It’s important to make sure that all of your pages can be crawled successfully by search engine robots. If they encounter any errors, they may not be able to fully crawl or index your site correctly.
You can use Google Search Console to check for any crawl errors and fix them if necessary. You can refer this guide to Google Search Console if you are not familiar with it.
Refresh Stale Content
Content that has not been updated in a long time is considered “stale” content. It’s important to regularly update your content to keep it fresh. This will help search engine crawlers understand that the content is still relevant and should be indexed.
It’s also a good practice to add new content on a regular basis in order to keep visitors engaged and interested in your site. This will help performance by increasing organic traffic and improving engagement metrics.
URL Structure
It is important to make sure that your URLs are SEO-friendly. This means they should be short, descriptive, and contain only relevant keywords.
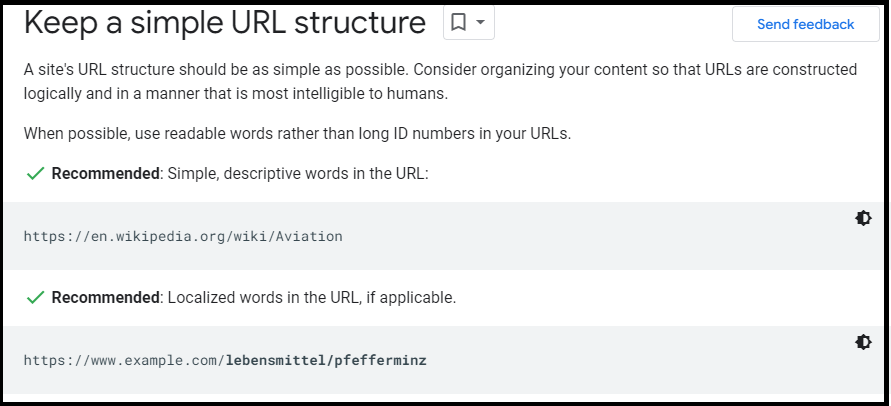
For example, instead of having a long URL like “example.com/products/mens-clothing/t-shirts”, you should use “example.com/mens-tshirts”.
Your URLs should also be structured in a logical way. For instance, you could have categories such as “Men’s T-shirts”, “Women’s T-shirts” and “Kids T-shirts.”
To optimise your URL structure, keep in mind these things:
- Use HTTPS Protocol
- Write Descriptive URLs
- Include Relevant Keywords
Use HTTPS Protocol
HTTPS is the secure version of HTTP and is recommended for SEO purposes. It helps to ensure that your site is encrypted and secure, which can help with online performance.
Some other benefits of using HTTPS protocol include
- Improved user experience
- Prevented malicious attacks
- Better trust signals
- Improved data in Google Analytics
Write Descriptive URLs
Descriptive URLs make it easier for users to understand what the page is about. This can also help online visibility by making your pages more crawlable.
For example, instead of having a URL like “example.com/product-222”, you could use “example.com/mens-tshirt”.
Include Relevant Keywords
Using relevant keywords in your URLs can help with SEO by making it easier for search engines to understand the content of your page. This may increase rankings and attract more organic traffic.
For example, if you have a page about “women’s shoes“, you could use the keywords “women” and “shoes” in your URL.
Topic Clusters
Topic clustering is a strategy that involves grouping related topics together. This means creating content around similar subjects and linking them to one another. Doing this will help search engine robots better understand the topic of your page.
It will also help visitors find more relevant information on your site, which can lead to improved engagement metrics.
Here are the steps needed to create your first topic cluster:
- Organise Your Resources
- Prioritise Your Most Important Keywords
- Gather Your Information
- Research
Organise Your Resources
Start by organising all of your content resources into clusters based on topics.
Group related blog posts, pages, and other content pieces together to create a comprehensive site structure.
Prioritise Your Most Important Keywords
Choose the most important keywords for each cluster and focus on optimising those first.
It’s best to first identify your first 2-3 topic clusters and then align them based on your 10 most important keywords.
Gather Your Information
Once you have identified your topic clusters, start gathering information to fill in the gaps.
Look for various sources to find content that you can use or adapt to improve user experience.
Research
Do some research (among your competitors) to find out what content is already being published on similar topics.
This will help you create better content that resonates with your audience and stands out from the competition.
Internal Linking
This is another powerful strategy to improve your site structure.
It involves linking various pages and content pieces on your website and it helps search engines to understand which pages are most important.
Internal links can also help visitors find relevant information and provide a better user experience, increasing the time they spend on your website.
But wait, there’s more.
A good internal linking structure also helps distribute the link equity of your pages more evenly, which can improve your site’s performance on search engines.
Do you want to know how it works?
Follow these best practices:
- Use Keyword Rich Anchor Texts
- Choose the DoFollow or NoFollow Tag
- Link to Relevant Content
- Power Up Your Pillar Pages
Use Keyword Rich Anchor Texts
Anchor texts are the words or phrases used to link your pages and content pieces together.
Make sure you use keyword-rich anchor texts to help search engine robots understand what each page is about.
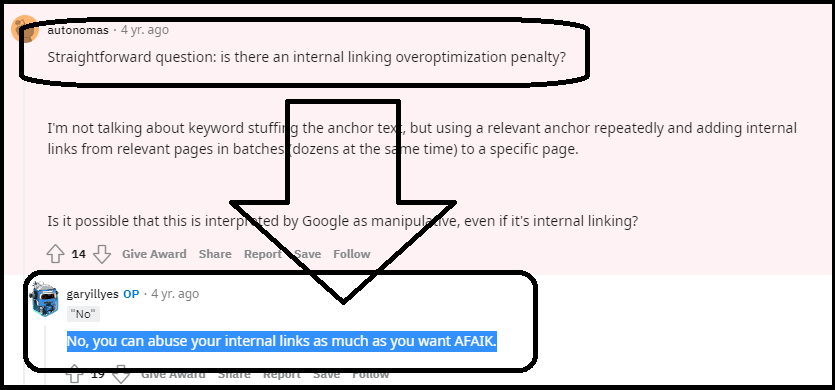
And remember, there’s no over-optimization penalty for leveraging keywords in internal links, as stated by Google’s Gary Illyes in his Reddit AMA:
Choose the Dofollow or Nofollow Tag
The power of your internal links depends on the link type.
Nofollow links don’t offer SEO value, but they can still help visitors understand which pages are more important and which ones to visit first.
Dofollow links are the ones that pass equity and help you rank better in search engine results pages.
Link to Relevant Content
Make sure you link your pages according to their relevance.
If you have a page about SEO, link it to other SEO-related topics. This will not only help search engine robots but also visitors, as they can find related information more easily.
Power Up Your Pillar Pages
Pillar pages are content pieces that provide an overview of a particular topic.
These pages usually include authority links and SEO-friendly anchor texts, which makes them perfect for internal linking.
Make sure you link your pillar pages to related content pieces as this will help its performance.
User Experience
Visitors don’t just come to your website to find information – they are also looking for an enjoyable user experience.
Your site structure should be easy to navigate and help visitors find what they’re looking for without any difficulty.
To do that, you need to create a hierarchy that is logical, and clear.
Make sure you save your visitors time by providing easy-to-follow navigation paths and avoid dead ends, which can be frustrating (and make people leave your website).
Keep these things in mind when working on your site structure to improve the user experience:
- Branding
- CMS and Design
- Navigation
- Sitemap
Branding
A good site structure can help you establish your brand and build trust with visitors.
So, create a hierarchy that is consistent and easy to navigate.
Choose colours and fonts that reflect your identity and make sure the navigation labels are clear and concise.
CMS and Design
Both the content management system (CMS) and design can have a huge impact on your site structure.
Choose a CMS with SEO-friendly features such as dedicated plugins and customised meta tags.
Also, make sure you use a user-friendly design that is optimised for search engines and helps user navigation.
Navigation
You should provide easy-to-follow navigation paths.
Create a hierarchy that helps visitors understand the content of each page quickly.
Make sure labels are clear and concise and include a search bar on every page to help visitors access content faster.
Sitemap
A sitemap can be an SEO-friendly way to provide a comprehensive overview of your site structure.
It should include all the important pages, posts, and categories that make up your website.
This will help search engines crawl and index your content more efficiently.
Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are SEO-related metrics that help measure the performance of a website.
These include page loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), which refers to the time it takes for a page to load
- First Input Delay (FID), which measures interactivity
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), which measures visual stability.
You can check your core web vitals data in Google Search Console and use it to improve your SEO performance.
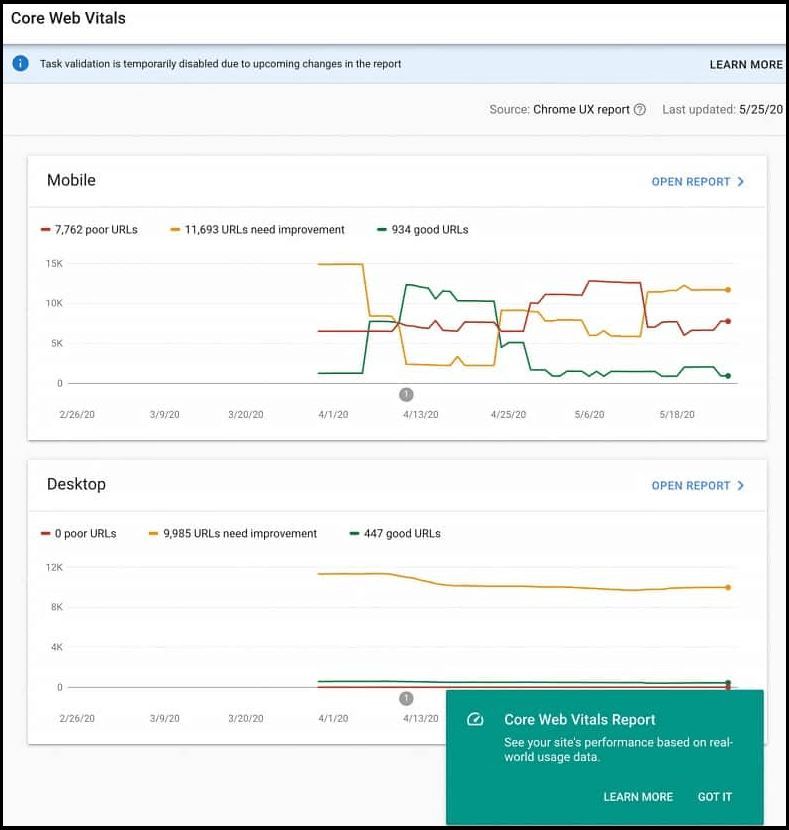
To do so, you should focus on these key factors:
- Images
- CSS and JavaScript
- Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Server Response Time
Images
Make sure your images are optimised by compressing and resizing them before uploading them to the website.
This will help improve page loading time and make your content easier to consume.
CSS and JavaScript
Minify your CSS and Javascript files, as this will reduce their size without sacrificing quality. This can also help improve SEO performance.
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Using a CDN will reduce loading time and make your content more accessible to users in different locations.
Server Response Time
Reduce server response time by optimising your database, caching static content, and investing in better hosting services.
This will ensure that visitors always have a smooth user experience.
Mobile-Friendly
Going mobile with your website can cost you time and money if you didn’t originally consider this when building your site, according to Google Search Central blog.
If you are using WordPress, going mobile is quite easy. You just need to use a responsive theme, which means that your website will look and work great on all devices, including smartphones, tablets, and desktops.
Always keep in mind these things when working on the mobile version of your site:
- Think With Your Thumb
- Keep the Design Simple
- Choose Fonts Wisely
Think With Your Thumb
When designing content for mobile devices, always consider how it will look when people use their phones.
Make sure to leave enough space between elements so users can tap on links and buttons easily.
Keep the Design Simple
Keep the design of your mobile site simple and easy to navigate.
Avoid clutter and long blocks of text as they could be difficult to read on smaller screens.
Choose Fonts Wisely
Make sure to use fonts that are legible and easy to read on mobile devices.
By following these site structure tips, you can create content that is optimized, looks great on all devices, and provides users with an enjoyable experience.
Page Speed
Page speed is a key SEO-related metric, as it affects how quickly content is loaded and displayed.
Optimising your site for page speed can be done by reducing the size of your images, minifying CSS and Javascript files, using a CDN, and reducing server response time.
If a page loads even one second too slow, it often results in fewer views and conversions, not to mention angry customers.
A slow website means you could be turning visitors away and dropping in SERP rankings.
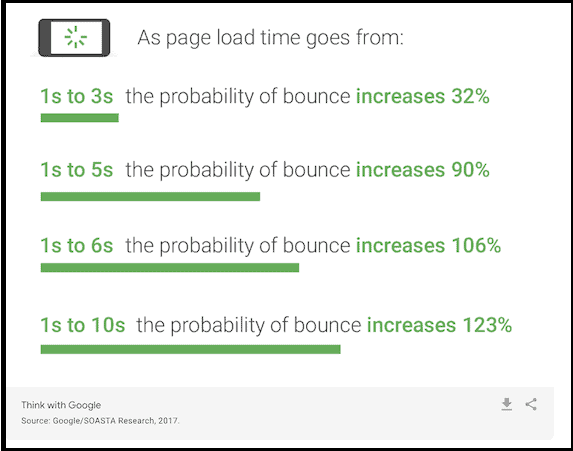
In fact, Google’s PageSpeed Insights research discovered that as a page’s loading time increases, the chance of someone immediately leaving (bouncing) also skyrockets.
Since 2010, Google has been using page speed as a ranking factor for desktop searches.
In 2018, Google developed the “Speed Update” to include page speed as a ranking factor for mobile searches too.
To measure your page speed, use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool. It will give you a score and make recommendations on how to improve it.
So, what is the recommended page speed?
Google suggests that pages should take two seconds or less to load (server response time).
To improve it, follow these tips:
- Enabling compression
- Reducing redirects
- Leveraging browser caching
Enabling Compression
Compressing files reduces the size of your web pages, images, and other items on your site by as much as 70%.
Reducing Redirects
A redirect is a response from a server that tells the browser to go to another page in order to find what it needs.
When too many redirects happen, they can slow down your site.
Reduce or eliminate unnecessary redirects to maximise your site performance.
Leveraging Browser Caching
Browser caching stores certain pieces of data (such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript) in the user’s browser so that it does not have to re-download them for every page view.
This can significantly improve page speed and user experience.
Your Turn: Work on Your Site Structure for Content SEO
Optimising your site structure is essential to make sure your site performs well in SERPs.
Remember, a well-structured site means content can be found quickly and easily by search engine bots as well as humans.
It also helps with page speed optimization and overall usability.
By following the tips included in this guide, you can create content that is SEO-friendly and delivers a great user experience.
Good luck!
