Search engines are smarter than ever before, and optimizing your content around keywords is no longer the best way to rank. Instead, semantic SEO is taking over.
Semantic SEO puts the user first. It’s all about optimizing content based on search intent and not search engines. The whole point of semantic SEO is to offer more relevant search results. When used correctly it can make a major difference to your organic traffic and rankings.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about Semantic SEO, including how you can apply a semantic SEO strategy to your website.
What is Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO is the process of creating content based on a topic instead of a specific keyword. When creating content for semantic SEO, more focus is placed on the search intent of the topic, with the goal of providing an in-depth piece of content that offers a user all the information they need.
While SEO in the past has been heavily focused on keyword optimization, search engines today can understand content based on its general topic. This means the way you write semantic SEO content is more focused on providing a quality, insightful resource – as opposed to stuffing keywords into a piece of content.
How Does Semantic SEO Work?
Content optimized for semantic SEO provides all of the information a user wants to know about a specific topic. It answers all of their questions and adds real value to their query.
An important feature of semantic SEO is that it isn’t focused on a specific keyword. Instead, semantic SEO content often ranks for a variety of related keywords.
This means semantic SEO content doesn’t only answer a user’s questions around their direct search query, but it also provides them with further information that they may be interested in. This practice is all about creating a complete guide on a topic, instead of just answering a single question or focusing on a very specific idea.
For example, you might type a search query into Google for “SEO”. Instead of only providing a definition of what SEO is, the best-ranking content will provide further information, such as how to create an SEO strategy, SEO tools you can use, SEO examples, and more. This is semantic content, as it covers the complete topic.
So, semantic SEO-optimized content covers every angle behind a topic and goes into the subject deeply. Instead of just trying to mention a keyword multiple times on a page, semantic content provides a more insightful and authoritative overview of the topic.
Why is Semantic SEO Important?
Search results pages can be highly competitive. With so much great online content, semantic SEO helps you create content with a greater purpose.
Google ranks pages based on their relevancy and authority. By optimizing your content for semantic SEO, your pages offer more value on the topic. This makes them more relevant and authoritative to Google to help you win the top spots in SERPs.
Ultimately, pages that take a semantic SEO approach achieve higher search engine rankings, attract more traffic, and provide more value to visitors.
Here are some of the main advantages of using semantic SEO.
Better Search Engine Rankings
First and foremost, effective semantic SEO can help your content to rank higher in search results pages. This is because your content is more insightful and valuable for the specific topic. It, therefore, offers a better resource for the topic model that the search engine has implemented.
Increases Your Keyword Scope
By focusing on a broader topic instead of a specific keyword, your content increases its chances of ranking for a wider range of search queries. This is because your content will answer more questions, and share a greater amount of information.
Writing around an entire topic instead of a specific keyword gives you more semantically-related keywords that apply to that topic. This means your content will show up in more searches, which results in it attracting more traffic.
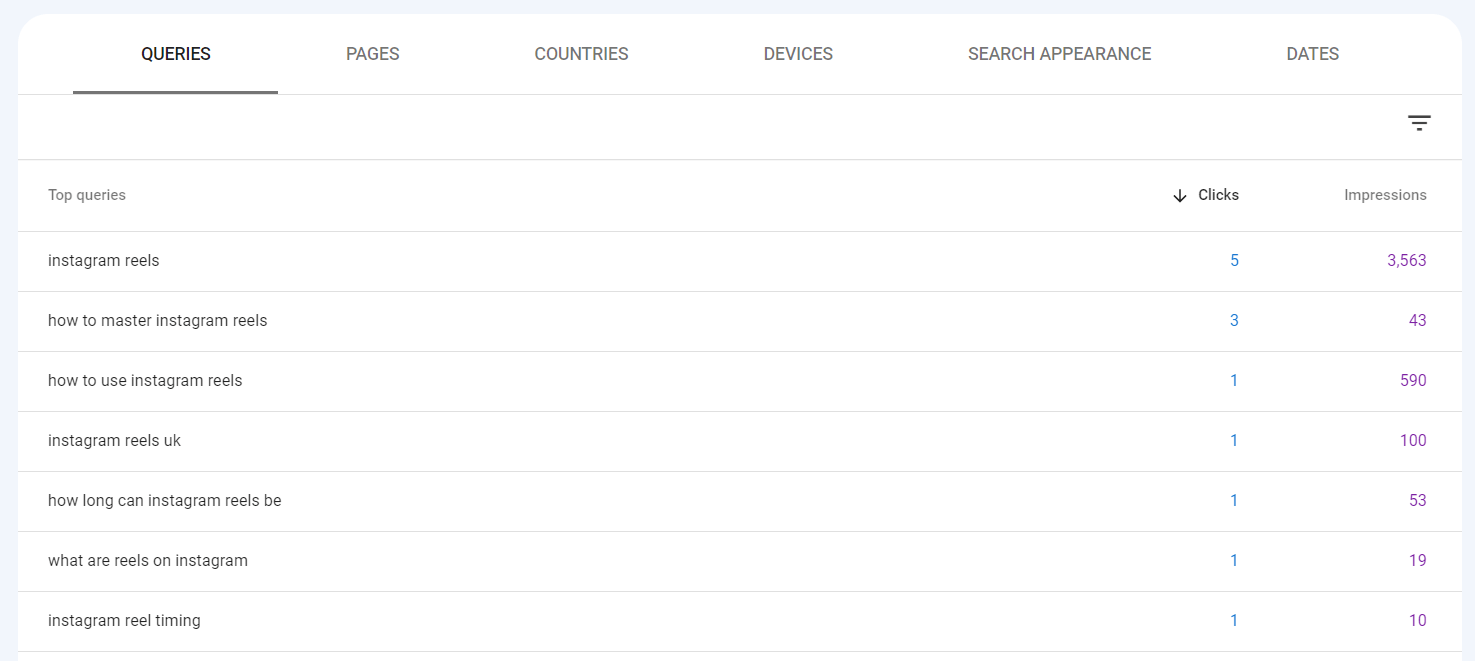
Just take a look at this Search Console report for a semantic SEO-optimized piece of content. The content ranks well for a variety of search terms, and not just a single keyword.
Your Content Appears in More Search Results Page Snippets
This is related to the point above. Google doesn’t only index relevant pages on its search results pages. The search engine also offers rich features in its SERPs – like list snippets, paragraph snippets, image packs, and video snippets. Here is an example of a featured paragraph snippet:
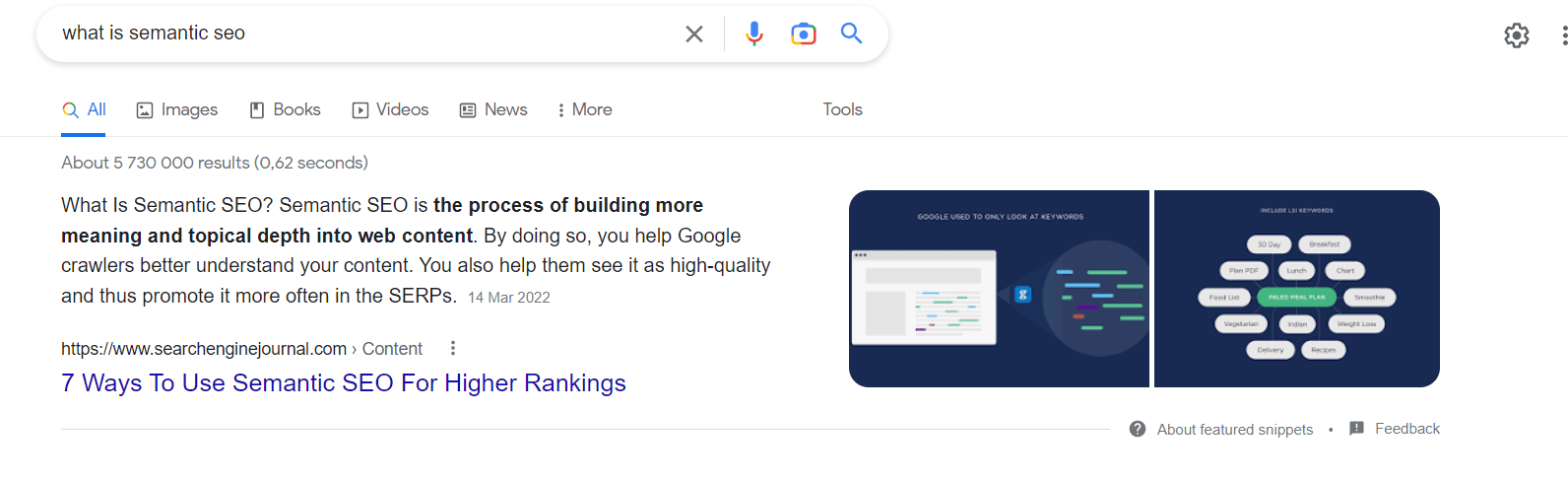
By covering a broad topic, your content directly answers more questions. This gives you greater opportunities to win these featured snippets, instead of simply getting your page indexed for a specific keyword.
Semantic SEO also improves your chances of being featured in the “people also ask” section in Google search results pages, like this:
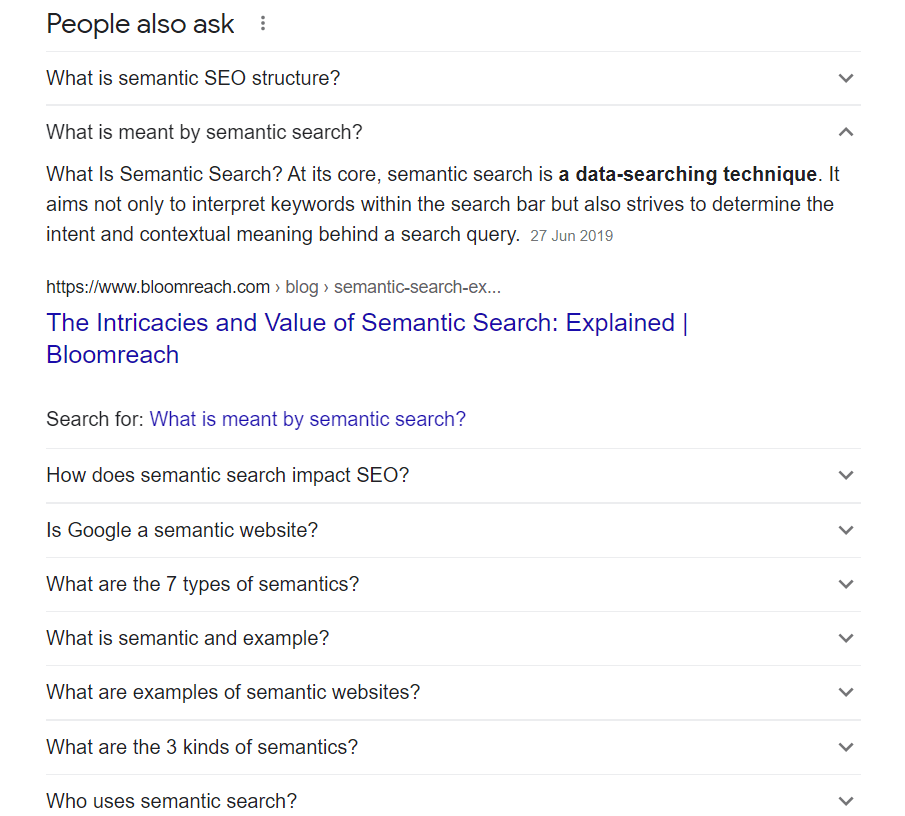
This is because your in-depth content should cover all of the important questions related to the topic, which these questions represent. If you optimize your content around offering a relevant, valuable, and insightful answer for every question on a topic, you’ll have a much better chance of earning these snippets.
Improves Your Topical Authority
Google doesn’t only rank content based on its keywords. Instead, Google’s algorithm places web pages with the most topical authority first.
If you publish in-depth content on a specific topic, your website will send greater topical authority signals to Google. This will help improve your rankings on content that covers that topic.
So if you create a new piece of content on the same topic as an existing semantic SEO-optimized piece, you’ll improve your chances of ranking with the new piece of content.
Visitors Spend Longer On Your Site
By covering a topic in full, you’ll provide more information to your visitors. This gives users more reason to scroll through your content and engage with your site.
If your content covers every angle of a topic, the user will naturally spend more time diving into the topic. This sends a valuable user experience signal to Google, which will help your content improve in rankings.
There’s a good chance this will also reduce your bounce rate, which will be helpful for improving your overall SEO.
Engages the User
This is related to the point above. In-depth content provides a greater scope of information on the topic. This helps you engage the user and generate more interest from them. At the same time, providing such insightful content on a topic also helps to establish trust with the user.
If you want to attract users with content and then get them to click on a CTA that moves them into your sales funnel, you’ll need to prove to the user that you’re a trusted expert in your field. Semantic SEO can help you achieve this.
Semantic SEO vs Traditional SEO
Semantic SEO and traditional SEO have a few key differences. Traditional SEO is focused on researching keywords and optimizing your website or content around those keywords. This is a highly targeted approach, where you aim to rank your pages for specific search queries.
More importantly, traditional SEO optimizes content for search engines, and not for the user.
Semantic SEO takes a broader user-first approach to SEO. This practice focuses on the user’s search intent and optimizes content around a topic, not search engines. This approach links your content to your user’s intent, which is the main difference between traditional and semantic SEO.
This is not to say that semantic SEO doesn’t use keywords though. Although it’s focused on the user, semantic SEO still relies heavily on keyword research. This is essential for understanding content topics and what users want to find out about that topic.
With regard to keyword research, the main difference is that traditional SEO targets a single keyword for each piece of content, while semantic SEO focuses on multiple keywords within a single topic.
Another key difference between traditional and semantic SEO is that semantic SEO focuses on providing deeper insights into an entire topic, while traditional SEO is more targeted towards a single idea. This means semantic SEO-optimized pieces of content offer more information in one place, while traditional SEO pieces are generally shorter. Traditional SEO content often includes multiple short articles that all fall under a broader topic.
Why Does Semantic SEO Exist?
Before we get into semantic SEO best practices, let’s first understand how semantic SEO came about.
An early SEO practice involves stuffing websites with keywords to help web pages rank for these terms. This actually worked, and many websites ranked for the right keywords, even though they didn’t offer the best content or solutions.
So, Google decided to change its algorithm to make sure better quality content took the top positions in the SERPs.
Google started developing advanced algorithms that consider a wide range of factors in order to rank content. Various algorithms crawl and rate sites in order to find the most relevant content for specific search queries.
This means the content you see in SERPs has been chosen based on what offers the most value to the user. This is where semantic SEO comes from.
Google’s algorithm update releases aim to improve the user experience on the search engine. Let’s unpack some of the key updates that have influenced semantic SEO.
Hummingbird
Google implemented the Hummingbird update in 2013 which essentially started the semantic search movement. This update incorporates natural language processing (NLP) into the algorithm to ensure web pages cover the topic properly, instead of relying on a bunch of keywords.
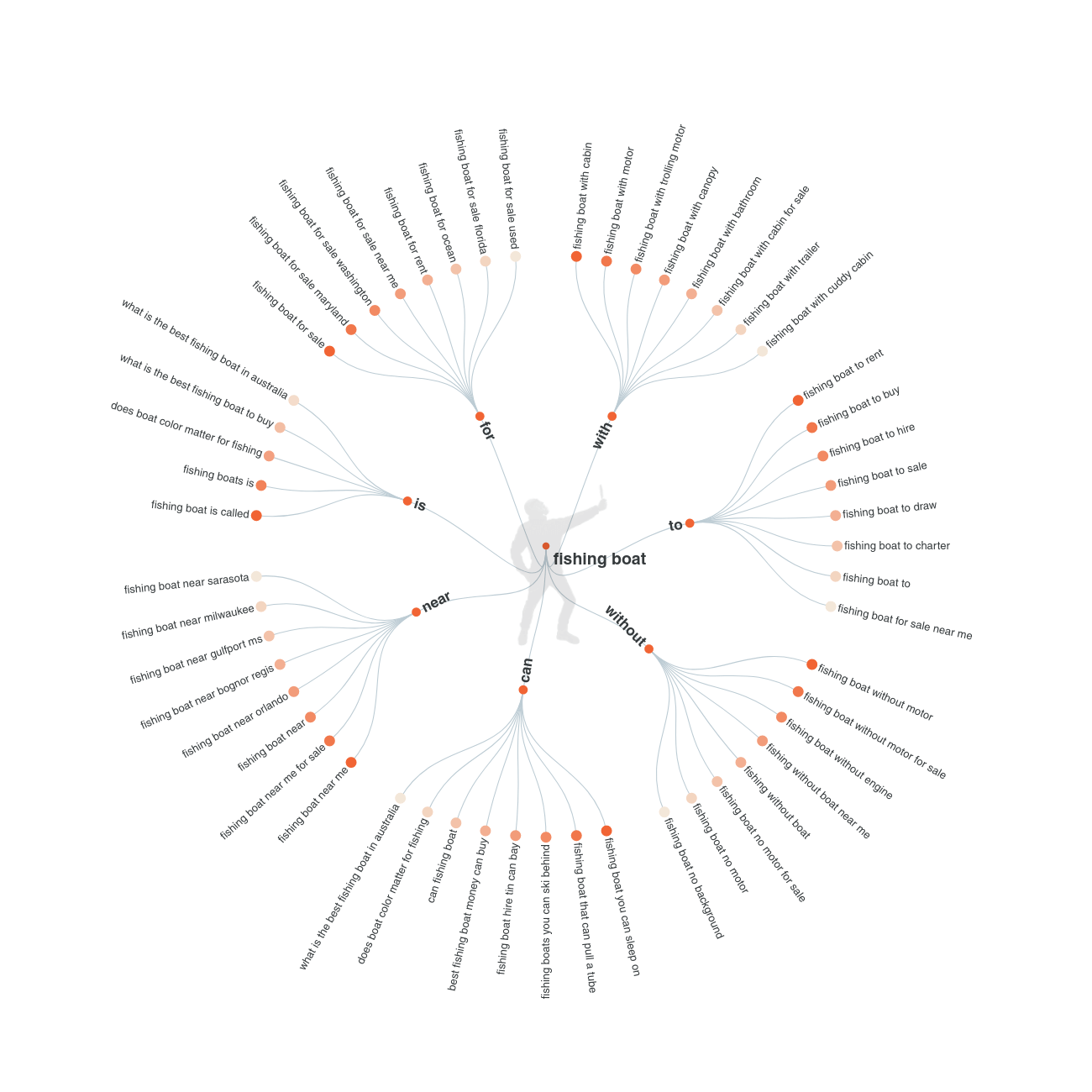
NLP basically incorporates a greater variety of natural words that are associated with the main keyword. For example, if your target keyword is “fishing boat”, chances are your content will also speak about terms like “water”, “vessel”, or “fishing rod”. These are NLP words.
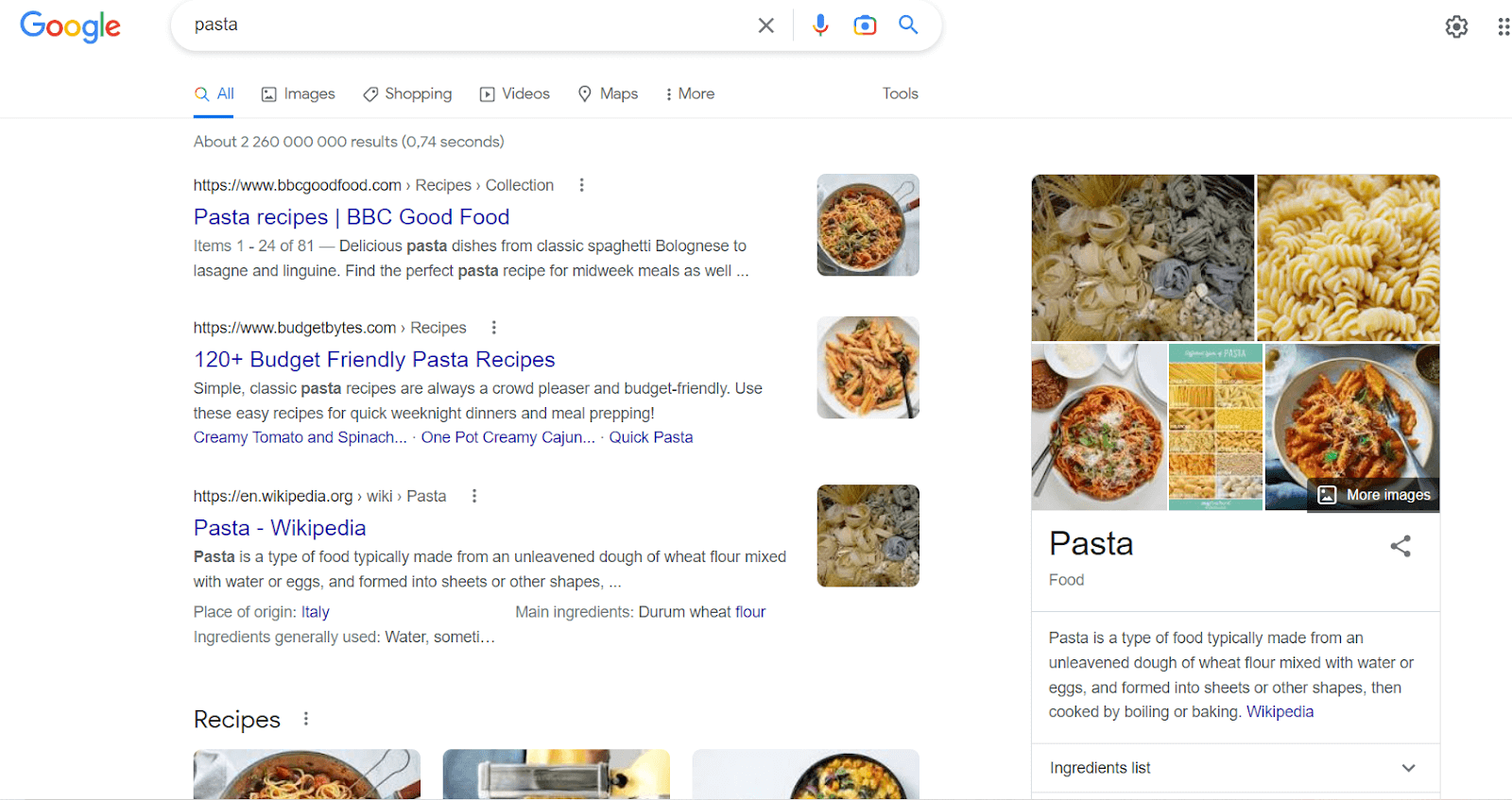
The Hummingbird update helped to make Google SERPs richer, by incorporating more data, such as the knowledge panel and recipes below:
RankBrain
Google rolled out the RankBrain algorithm update in 2015. This saw the search engine’s algorithm adopt machine learning and AI technology to deeper understand the user’s intent behind their search query.
RankBrain does this by finding the best-performing search result items for each query and using this to ensure only the most relevant content is displayed for each search result.
BERT
Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) was introduced in 2019. This algorithm update interprets and understands search queries on a deeper level through NLP technology. This smart algorithm can identify the relationship between words in search queries to figure out exactly what the user wants to discover with each query.
Overall, each of these algorithm updates has made Google smarter and more “human-like”, which means the search engine understands the intent behind search results (instead of just matching keywords). This is what has resulted in the value of semantic SEO.
How to Use Semantic SEO
Semantic SEO may seem pretty complex when you think about Google’s algorithm updates, but it’s actually a straightforward idea to put into practice. Here are some of the steps you need to take when incorporating semantic SEO into your content plans.
- Understand User Intent
The most important thing to get right about semantic SEO is understanding the user’s search intent and creating relevant content that matches this. Because Google takes relevancy so seriously, you have to carefully target search intent when developing content.
Once you have established your semantic SEO keywords/topic, do some deep research into them. Understand what kind of questions the user wants to answer, what kind of related topics exist, and what kind of angle the user is looking for. Do they want informational content? Are they looking for product recommendations? All of this adds to the user’s intent.
Once you understand exactly what the user wants to get out of the content, you can start to create content that matches this.
- Create Detailed Content
The next step in your semantic SEO strategy is to dive deep into the content topic. The more detailed you go into a content topic, the stronger your semantic SEO content will be.
To do this, you’ll need to spend some time researching the topic and come up with all of the questions or sections of information that a user might want to know about the topic. The more related sections you include, the more insightful and in-depth the content will be.
While detailed content is valuable, you also don’t want to overdo it and offer too much information to the point that it becomes irrelevant. This could actually negatively impact the user experience, which won’t help your content in the SERPs.
Many top-ranking recipes offer a great example of semantic SEO content. Let’s say you run a Google search for “fish tacos”, you’ll get results that look something like this:
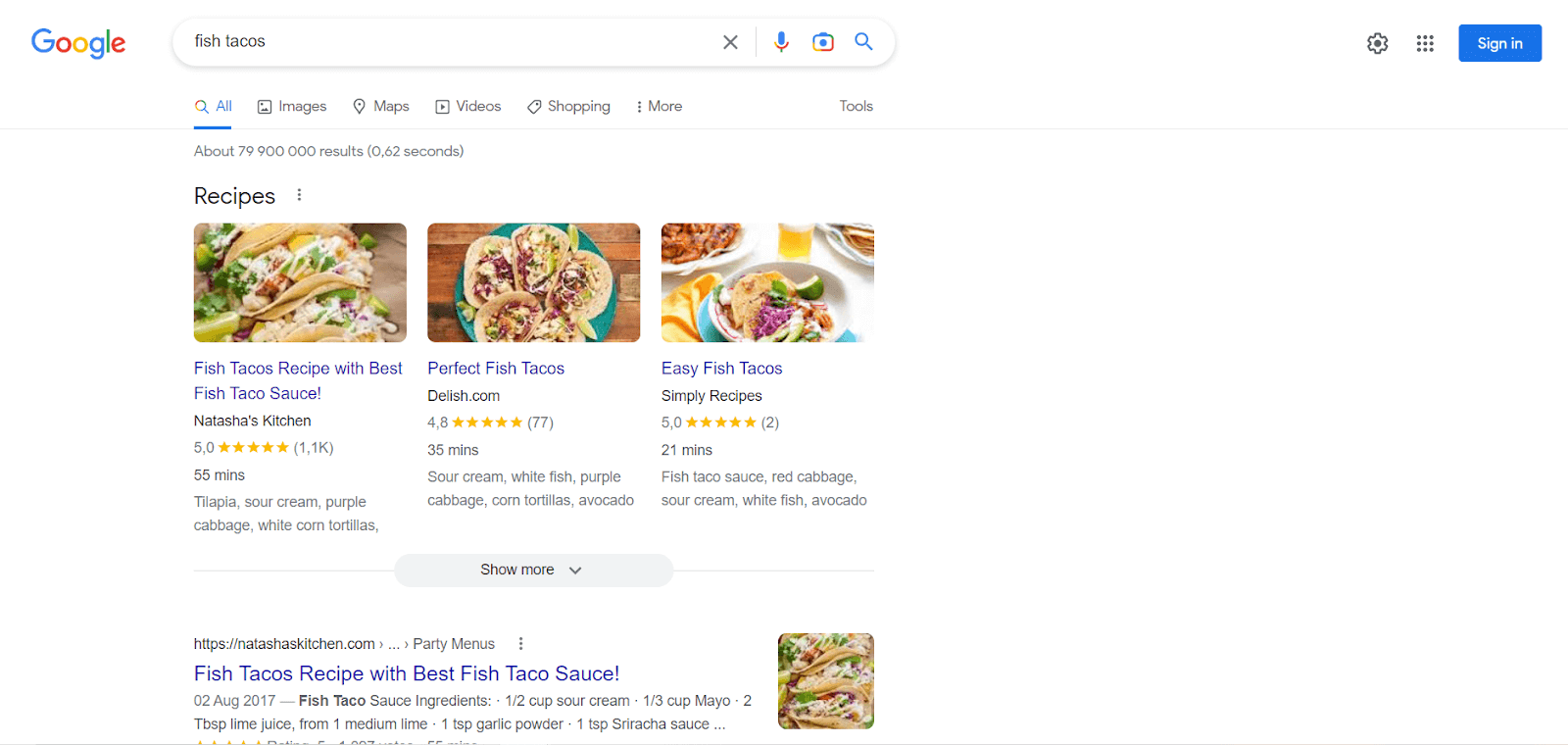
The top-ranking search result does include a tasty recipe for fish tacos. The page that the recipe is on also includes additional information on the topic of fish tacos, such as a back story of the author’s love for tacos, and a detailed taco ingredient list.
This all adds further information on the topic that the user might be interested in, which helps to make it an authoritative and NLP-friendly source on the subject of fish tacos.
Here’s a great tool to help you understand related subtopics and information related to a certain topic or keyword. Adding this information to your content can be incredibly valuable for your semantic SEO strategy.
Of course, you should also just do plenty of research the old-fashioned way – Google your topic and take note of all the information that the top-ranking pages are covering.
- Extend Your Keyword Research
As we’ve already mentioned, semantic SEO-optimized content often ranks for multiple keywords. This presents an excellent opportunity for you, as it allows you to incorporate a greater variety of keywords into your content.
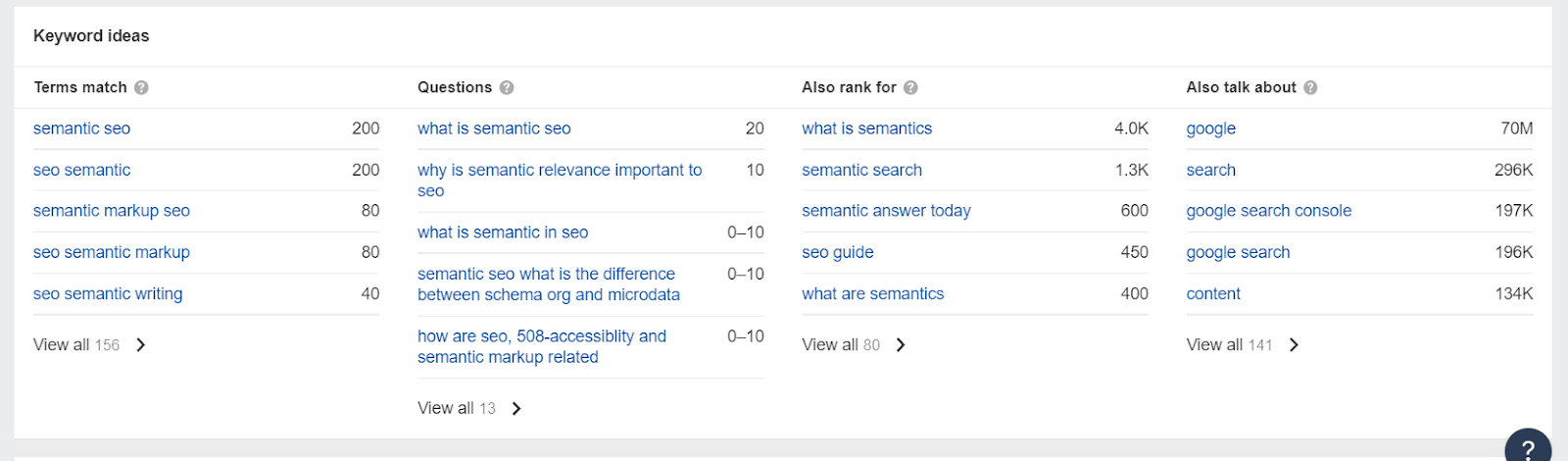
Once you have established your main topic and target keyword, look for additional keywords that support this. You could find these as suggested results in keyword research tools, like this:
Or through doing some digging on Google search results pages.
One easy way is to simply type your keyword or topic into the search bar, and see what other recommended topics are generated, like this:
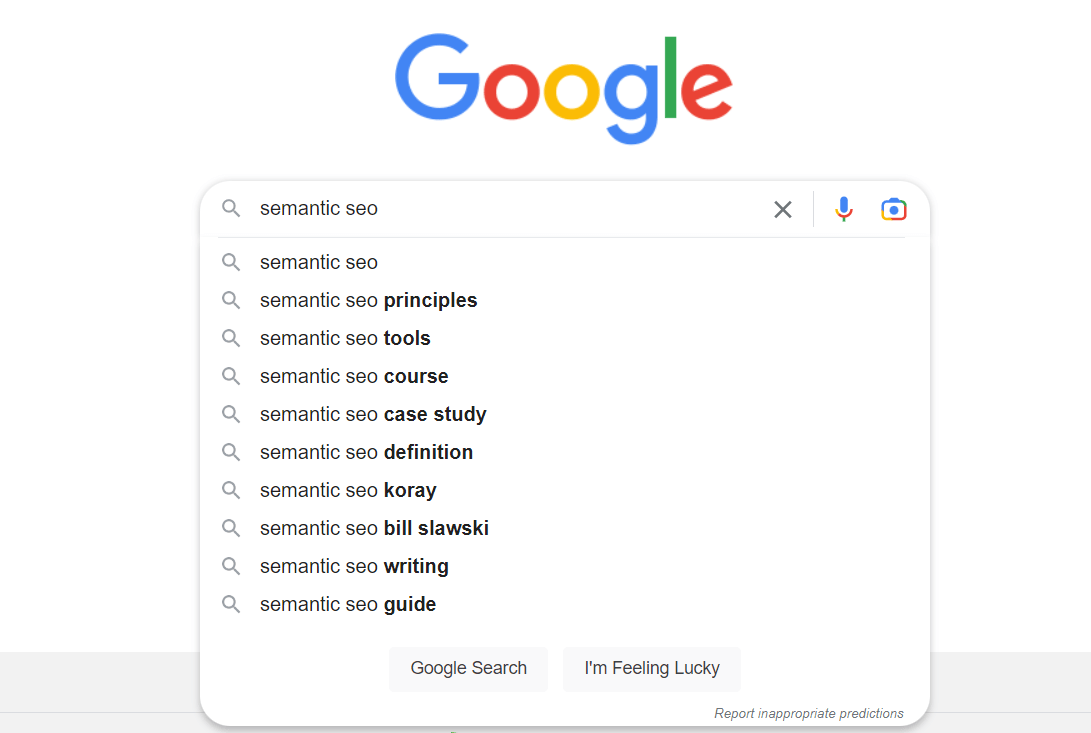
Each of those recommendations is a popular search query based on your main topic, so they offer possible additional keywords that you can incorporate into your content.
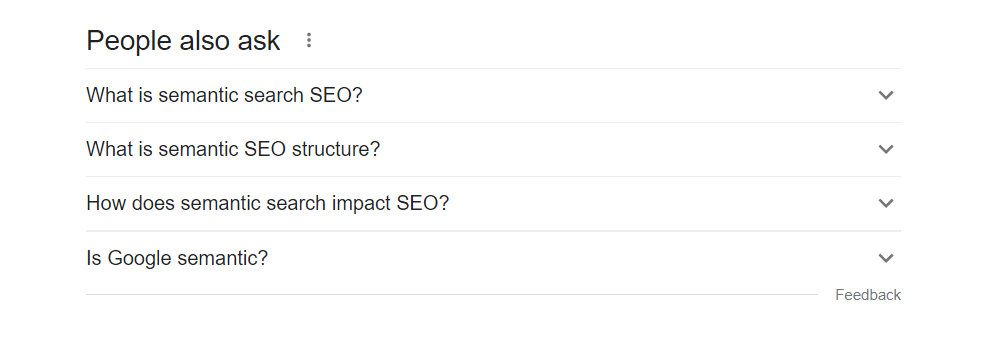
Other places to find extra keywords could be in the “People also ask” section, like this:
As well as the related search queries at the bottom of the results page, like this:
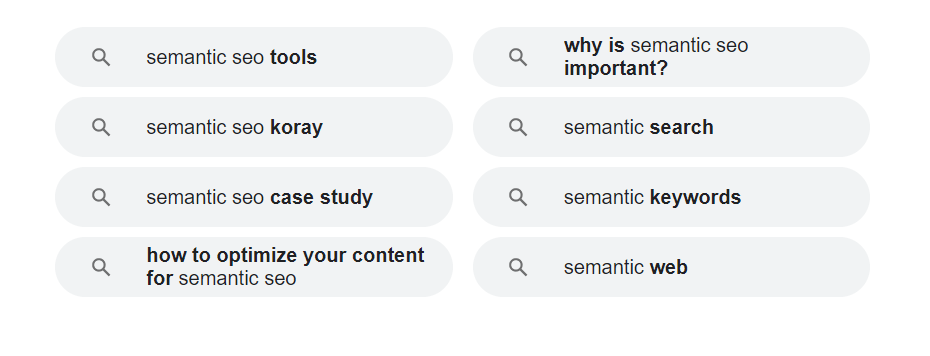
These are all valuable keywords that you can add to your semantic SEO content to increase your search engine exposure.
- Create Structured Data for Your Content
Structured data (Schema) is a method of classifying the data on your web pages to help search engines understand the data more easily. This can help search engines display relevant information in the best way possible, which can help you win rich snippet positions for your content.
Rich snippets include sections like this:
Or this:
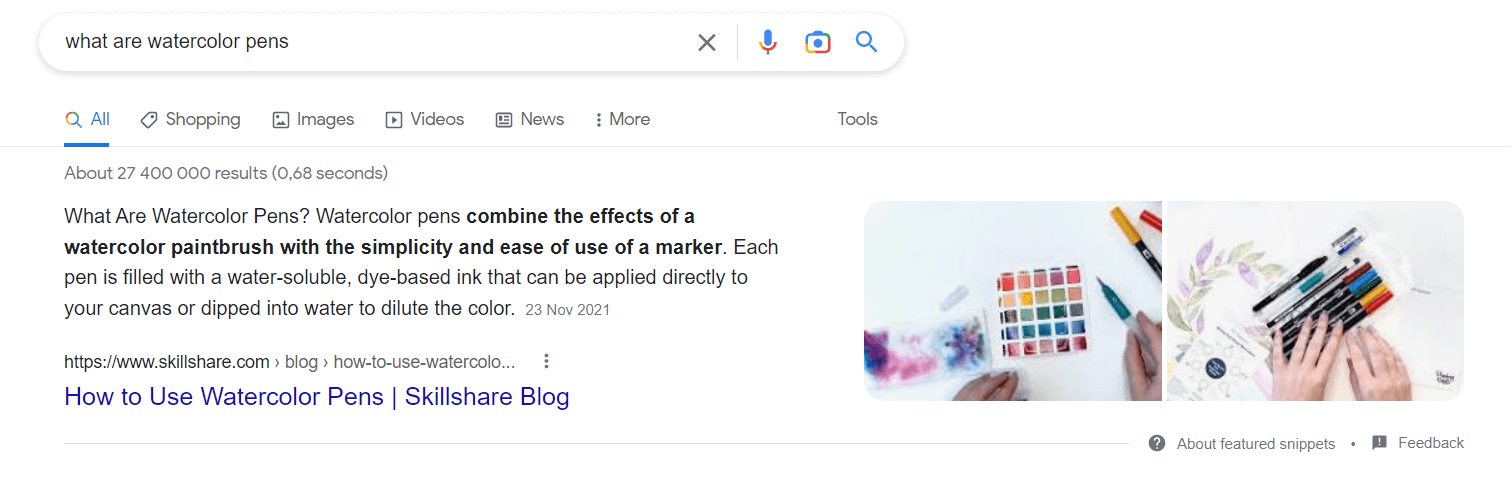
Schema.org can help you create the right structured data for your content. There are also various WordPress plugins available to help you create structured data.
This is a relatively easy way to help search engines understand and index your content correctly. And if this content is strong enough, it could win the valuable rich snippet positions in Google.
- Optimize Your Content
Publishing your semantic SEO content is only the first step. If you want it to perform at its best in search results, then you’ll want to optimise your existing content over time. Doing this can help you identify a greater scope of search terms that you can incorporate into your content to attract more traffic.
A good strategy is to wait two weeks to a month until your page is indexed. Then run it through Google Search Console and see what search terms people are using to discover your content.
This could reveal potential new keywords to add to your page. Also, be sure to research the top-ranking pages for your topic to see if they offer any information that you don’t.
By consistently updating your page, you’ll be able to ensure it’s the best possible resource on your subject matter. This is critical for effective semantic SEO.
- Use a Strong Internal Linking Strategy
Internal linking helps add relevance and authority to your content. When a search engine crawls your site, it can use your website’s internal linking structure to help understand which pages are most important.
If you have a lot of relevant pages on your site linking out to an important page (which is semantic SEO-optimized), then this page will hold more authority on your website. This can help search engines boost this page’s ranking.
When performing your internal linking structure, there are two important things to keep in mind:
- Anchor text: Try to add your link over relevant anchor text (your keyword or topic) to help search engines add more topical authority to the page
- Structure: Many sites follow a structure with important pillar pages (your semantic SEO content) with multiple cluster pages linking to that main pillar content. This is also known as a hub and spoke structure. Ensure the cluster pages are relevant to the pillar page and that all relevant pages link toward it. This will help your site convey a flow of topical authority to search engines
Conclusion
Just like Google’s algorithm, SEO is forever changing. While there are always new ways to improve your content to achieve the best possible organic rankings, one factor will always remain true – your user experience is vital.
As long as you understand what the user wants to get out of your content and you optimize your content for the user, you’ll have a great chance at attracting maximum traffic to your website. At its core, this is what semantic SEO is all about.
